Research results show that brain neurons are destroyed when drinking deeply for 10 consecutive days

Although there is a saying that 'alcohol is the chief of a hundred medicines', it is not known in detail how alcohol actually affects the body, and research is still ongoing at the time of writing the article. Experiments have confirmed that ingesting large amounts of such alcohol every day destroys neurons (nerve cells) in the brain and induces anxiety.
Daily alcohol intake triggers aberrant synaptic pruning leading to synapse loss and anxiety-like behavior | Science Signaling
Ten days of binge drinking disrupts neuron connections, causes anxiety and other cognitive problems
https://www.zmescience.com/science/biology/binge-drinking-synapse-disruption-0523532/
The research was presented by a research team led by Joao Relvas, a senior researcher at the Department of Cellular and Molecular Biology, University of Porto, Portugal. To investigate the effects of alcohol on the brain, Relvas and colleagues fed male mice with alcohol or water in tubes for 10 consecutive days. Mice in the alcohol-fed addict group ingested 1.5 grams of alcohol per kilogram of body weight.
Then, while the mice fed only with water showed almost no change, the mice fed with alcohol showed synaptic dysfunction, and the behavior reminiscent of anxiety increased visibly. thing. Therefore, when we analyzed the brain tissue of mice, we found that ingestion of a large amount of alcohol destroyed nerve cells in the prefrontal cortex , which is the most important part of the brain, by microglia .
Below are pictures of water-fed mouse microglia (left) and alcohol-fed mice microglia (right). The photo on the right shows microglia involving nerve cells in the prefrontal cortex.
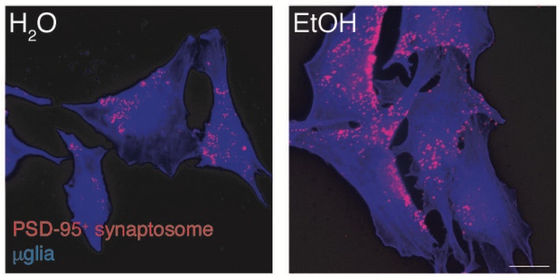
Microglia, which exist in the brain and spinal cord, are one of the
'Alcohol-induced synaptic dysfunction reduced neurotransmission and increased anxious behavior in mice. High alcohol intake activates microglia that disrupt neuronal connections, causing anxiety. It suggests that it is inducing. '
They also found that when the research team administered pomalidomide , a treatment for multiple myeloma , to mice, it blocked the production of a substance called TNF that causes inflammation and did not disrupt synapses.
The researchers argue that the results of this study suggest that drugs that regulate TNF may help treat alcoholism and mitigate the effects of alcohol on the brain, and need to be investigated in human clinical trials. It states that there is.

However, 'A large amount of alcohol intake has an adverse effect not only on the brain but also on the heart, liver, pancreas, and immune function. Therefore, even if it helps alleviate the effects on the brain, it is a TNF inhibitor for drinkers who drink alcohol every day. Should not be administered easily, 'Relvas said. 'The best cure for problems caused by alcohol is prevention, as long as you moderately control your alcohol intake or don't drink at all,' the research team said.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1i_yk