Research results show that the real reason for goosebumps is to grow hair, which may shed light on baldness treatment

Recent research has revealed that there is a previously unknown mechanism and role behind the
Cell Types Promoting Goosebumps Form a Niche to Regulate Hair Follicle Stem Cells: Cell
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(20)30808-4
The hair-raising reason for goosebumps is revealed – Harvard Gazette
https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2020/07/the-hair-raising-reason-for-goosebumps-is-revealed/
Science May Have Finally Explained The Reason Why We Still Get Goosebumps
https://www.sciencealert.com/science-may-have-finally-explained-the-reason-why-we-get-goosebumps
NTU researchers seek clues on hair loss in goosebump phenomenon - Focus Taiwan
https://focustaiwan.tw/sci-tech/202008060013
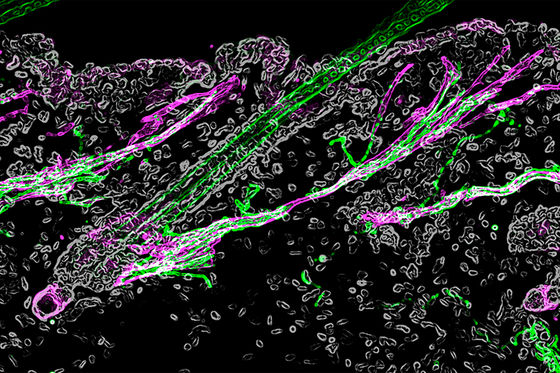
'The skin is a truly fascinating system. The skin that separates our bodies from the outside world has stem cells surrounded by a wide variety of cell types,' says Harvard University biologist. Mr. Ya-Chieh Hsu. Hsu et al.'s research team used high-resolution electron microscopy to observe mouse hair follicles in order to investigate in detail the mechanism by which the skin protects itself by adapting to external temperature changes.
Below is a micrograph of a mouse hair follicle actually taken by Mr. Hsu et al. The green colored part is the sympathetic nerve, which is involved in the mechanism of goosebumps, and the purple part is the arrector pili muscle, which has the function of making the hair stand on end.
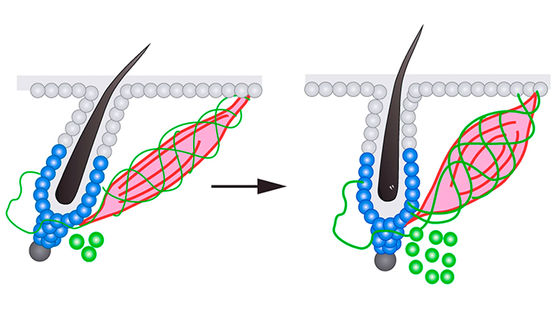
Previous research has shown that goosebumps are caused by the arrector pili muscle, which is stimulated by the nerves, raising the skin, but this research shows that the arrector pili muscle, which is stimulated by the nerves, causes goosebumps to rise up on the skin. It has been found that 'stem cells', which have both the ability to proliferate and the ability to differentiate into other types of cells, are also involved in the mechanism that causes goosebumps.
The following is a diagram of the mechanism. When you feel the cold, the pink arrector pili muscle contracts, which causes the skin to go from normal on the left to goosebumps on the right. This research further revealed that when goosebumps appear, green sympathetic nerves release neurotransmitters that act on blue hair follicle stem cells, which activates hair follicle stem cells and promotes hair growth. Ta.
Dr. Hsu said, ``It was a big surprise to discover that neurons and stem cells interact in a synapse -like structure by observing them at the ultrastructural level. This is because it typically connects with excitatory cells that have synapses, like muscles, and it is extremely rare to target cells like hair follicle stem cells.'
Researchers added to the conventional theory that ``goosebumps were caused when humans still had body hair and created a layer of air to keep them out of the cold.'' We believe that the long-term strategy of 'promoting hair growth and increasing hair volume to cope with future cold weather' is related to the mechanism that gives goosebumps.
In addition, when the research team conducted an experiment to remove the pili muscle from the hair follicle of the mouse, the result was that the connection between the sympathetic nerve and stem cells was also lost. Since it is known that the piloerection muscles in the hair of men with alopecia are also very weakly responsive, co-author of the paper, Professor Sung-jan Lin of National Taiwan University, has clarified the mechanism by which alopecia occurs. We believe that there is a close relationship between the functions of the arrector pili muscle and the sympathetic nervous system.
Professor Lin said, 'This study revealed that hair follicle stem cells are activated by receiving signals from sympathetic nerves via ADRB2 receptors .' He expressed the view that by developing a drug that reduces hair loss, it may be possible to effectively treat hair loss.
Related Posts:
in Science, , Posted by log1l_ks