What are the five points to keep in mind when reading scientific articles?

by
New facts revealed by researchers around the world through research and experiments are known to a wide range of people through articles such as magazines and online media. Hassan Vally , an associate professor of public health at the University of La Trobe , has compiled a summary of the “five precautions” that should be taken into account when reading such articles on medicine and science.
Is this study legit? 5 questions to ask when reading news stories of medical research
https://theconversation.com/is-this-study-legit-5-questions-to-ask-when-reading-news-stories-of-medical-research-117836
◆ 1: Is the research peer-reviewed?
Peer review is a review of papers by experts in the field and evaluates the scientific validity of the research. Academic journals in which articles are published include peer-reviewed and unreviewed journals, but articles published in peer-reviewed journals are checked by two to three reviewers. In this case, if a serious defect is found in the method or content of the research, the publication of the paper will be suspended or the researcher will correct the problem.
Some have pointed out that peer review of papers is not all-round, but peer review of papers can be an indicator to trust research results. “If the research featured in the article is not peer-reviewed, please read a little discount,” Vally said.
Pointing out that `` thesis peer review system is not universal ''-GIGAZINE

by Free-Photos
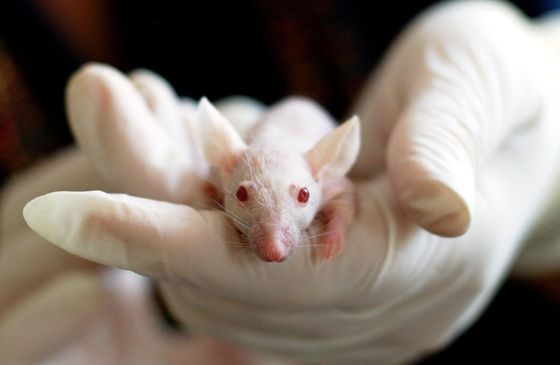
◆ 2: Was the research conducted on human subjects?
In the early stages of medical experiments, instead of suddenly conducting experiments on humans, laboratory animals such as mice and cells cultured in the laboratory may be used. This type is only an early process of scientific discovery, and it cannot be short-circuited to be “similar to humans because it has been demonstrated in mice”.
by
◆ 3: Does the survey result indicate a causal relationship?
What is important in research related to people's daily lives is whether they have just discovered a correlation or is there a causal relationship ? For example, in a study that “coffee people are prone to heart disease”, whether “coffee drinking causes heart disease” or “simply drinking coffee has a high probability of heart disease” You need to pay attention.
A study on the relationship between coffee and heart disease found that “coffee drinkers are more likely to have a smoking habit, resulting in a correlation between coffee and heart disease”. In this way, there is a possibility that factors other than the ones focused on in the research overlap by chance and cause a specific result, so “whether the research showed a causal relationship or a correlation. It should be emphasized that it is only found.

by
◆ 4: How big is the effect?
In medical articles, attention tends to be focused only on the consequences of a specific action, but it is also necessary to understand the “how much it actually works”.
For example, if it is written that “the act of A increases the risk of illness of B by 50%”, it is easy to think that “A is terrible”. However, if the original risk of the disease B is very small, a 50% increase in risk may not be a problem. If the initial risk of the disease B was 0.1%, Vally points out that even if the risk increases by 50%, it is only 0.15%, not so dramatic.

by Lukas
◆ 5: Is the research result supported by other studies?
In science, the accumulation and support of many scientists is important, and no matter how innovative the research results are, they cannot make a definitive evaluation by themselves. Only when other researchers conduct reproducible experiments and the findings are supported by experiments conducted in different environments and approaches, the credibility of the research results is born. Instead of jumping to a conclusion with just one study result, Vally said it was important to wait and interpret it after many studies have confirmed it.

Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







