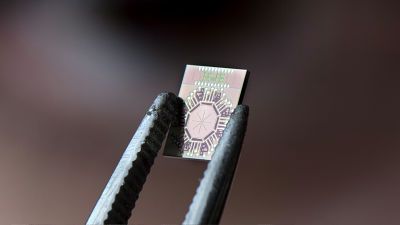
MIT Develops 'Rectenna' Using New Material to Convert Received Wi-Fi into Electric Power

by Riccardo Annandale
A device that converts radio waves into direct current is called " rectenna ", and it is used for wireless power supply etc. Newly developed by MIT is a rectenna using materials suitable for Wi-Fi frequencies of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band, in the case of 150 micro watts which is the strength of general Wi-Fi, 40 micro It can generate electricity of watt.
Two-dimensional MoS 2 -enabled flexible rectenna for Wi-Fi-band wireless energy harvesting | Nature
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-0892-1
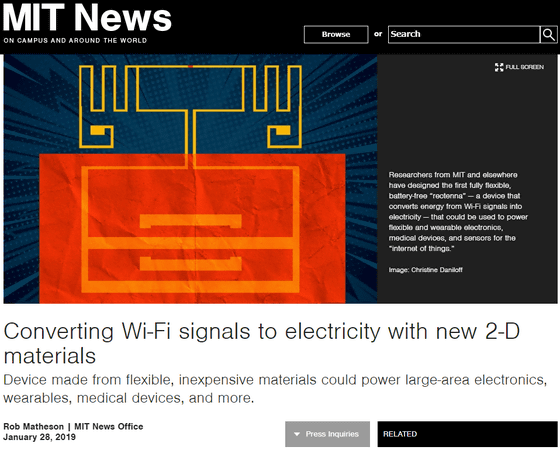
Converting Wi-Fi signals to electricity with new 2-D materials | MIT News
http://news.mit.edu/2019/converting-wi-fi-signals-electricity-0128
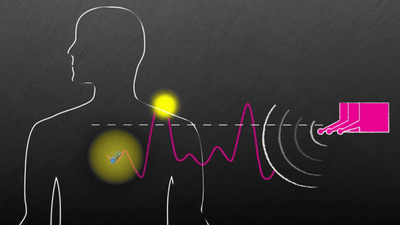
Rectenna is an "antenna with a rectifier", which converts radio waves received by an antenna into DC current through a rectifier circuit. The idea of using radio wave energy for power generation is not specially new, and in the past a number of rectennas have been developed.
In conventional rectennas, silicon and gallium arsenide have been used for rectifiers. Even with such a material, Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz band and 5 GHz band can be covered but lack flexibility, even if it is suitable for making a small terminal, cost aiming at enlarging such as covering the surface of buildings and walls It will be outrageous.

by Morteza F.Shojaei
On the other hand, in the case of flexible materials, it will not operate unless it has a low frequency, and Wi-Fi signal can not be converted.
For this reason, MIT uses molybdenum disulfide to create atomically thin ultrahigh-speed Schottky barrier diodes . Thanks to this, we have created a flexible rectifier that covers radio waves in the frequency bands that are flying in everyday life, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE.
According to MIT, output efficiency is about 30% to about 40% at typical Wi - Fi intensity. In the case of a rectifier using silicon or gallium arsenide, the efficiency is somewhat low, as it achieves about 50% to about 60%. In the future, the research team is aiming for further improvement in efficiency.
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by logc_nt