Successful development of extremely small wireless sensor capable of implanting in the body with amazing sand grain size

The University of California at Berkeley succeeded in developing an ultra-small wireless sensor of 1 mm square which can transmit data to the outside through ultrasound, record the electrical signal flowing through the nerve by embedding it in the body, and need no battery.
Wireless Recording in the Peripheral Nervous System with Ultrasonic Neural Dust: Neuron
http://www.cell.com/neuron/abstract/S0896-6273(16)30344-0
Engineers Create The First Dust-Sized Wireless Sensors That Can Be Implanted Into The Human Body
http://sciencenewsjournal.com/engineers-create-first-dust-sized-wireless-sensors-can-implanted-human-body/
You can see the actual size and structure of the extremely small wireless sensor by looking at the following movie.
New "Neural Dust" sensor could be implanted in the body - YouTube
Just thinking of men will manipulate the robot arm and eat something from the spoon. This will allow you to move electric prosthetic hands etc. just by thinking by reading the brain signal "Brain machine interface(BMI) "in the future, it is a technology that has not yet been realized.

The wireless sensor below as extremely small as possible to inject into the body that was developed as hardware capable of realizing such BMI. You can see how small parts you put on your fingertips.
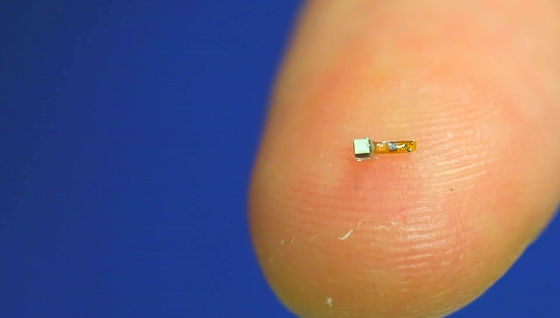
Compared with coins, it is just about the size of sand.

While this extremely small size, wireless communication by ultrasonic wave is possible and battery is unnecessary.

It is thought to work even when implanting in the human body.

Sensors embedded in the body measure and send various data in real time.

Below are the wireless sensors implanted in the rat's body measuring electrical signals through nerves in the body.

Also, if you use extremely small wireless sensor, even people with symptoms such as limb paralysis have the possibility to be able to move using artificial orthotics such as electric prosthetic hands.

In recent years there are IoT devices that can measure health care logs like Fitbit, but with this extremely small wireless sensor you can record up to the electric signals of nerve cells in the brain, and always have finer health care data than the activity meter I can track it.

Ultra-small Wireless Sensor converts ultrasonic waves into built-in piezoelectric crystals into extremely small electricity and becomes power of transistors connected directly to peripheral nerve and muscle fibers. If injected into peripheral nerves and muscles, data can be wirelessly transmitted to the outside using ultrasound.

Recorded electrical signal data is analyzed and transmitted, and it is distinguished as different separate electrical signal data.

With this feature, it is said that you can move the electric prosthesis etc just by considering it with a person with paralysis.

In the future we will be developing a more sophisticated and compact sensor to implant in the brain. The current sensor is 1 mm square, but it needs to be downsized to 50 microns in order to implant in the brain and central nervous system.

One material seems to work throughout the life once implanted.

Also, the extremely small wireless sensor has the possibility to cooperate with various medical equipments and software. For example, if you embed sensors one by one in individual organs, you will always be able to grasp the health status of each organ ... ....

How to use such as suppressing appetite by stimulating nerves, controlling bladder function.

It is thought to be effective in controlling symptoms such as epilepsy.

Related Posts: