"Reproducibility" of science is at stake

ByCarlos Henrique
In 2015, a group of psychological researchers attempted to reproduce the latest 100 psychological research papers,39 experimental results could be reproduced. I can not necessarily say that the original report was wrong, but in the science fieldReproducibilityIt has turned out that there are many problems concerning the problem. So, Nature of the comprehensive academic journal made a questionnaire to 1576 scientists "Do you feel a crisis in contemporary reproducibility?" "What do you think is the cause?" And publish the results .
1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility: Nature News & amp; Comment
http://www.nature.com/news/1-500-scientists-lift-the-lid-on-reproducibility-1.19970
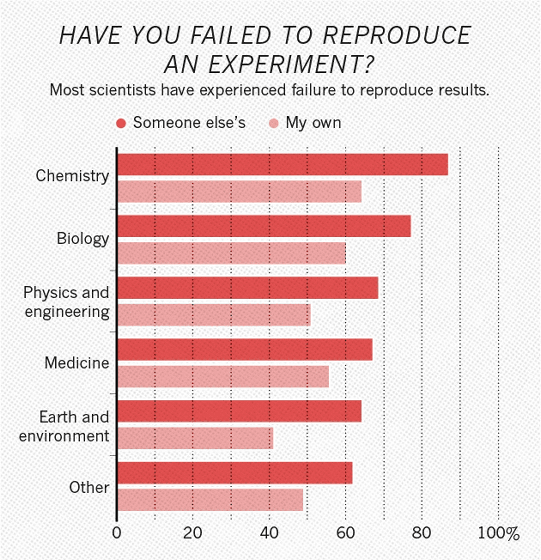
According to a study by Nature, among the 1,576 researchers surveyed, the proportion of researchers who have failed to reproduce the experiments announced by scientists other than themselves was 70% or more, and 50 % Or more failed to reproduce the experiment that he himself performed.
Reproduction failure experience in each field is as follows. The results of the survey for each category of chemistry, biology, physics & engineering, pharmacy, global environmental studies and others show that the proportion of failure to reproduce in chemistry and biology is relatively high
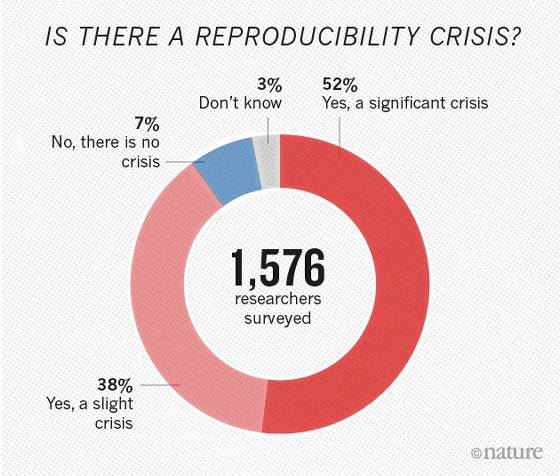
And 52% answered "Yes, it is pretty crisis" to the question "Is scientific reproducibility in the danger?", "Yes, it is on the verge of a little crisis" 38% answered that "No crisis" is 7%, many researchers felt a crisis. On the other hand, less than 31% of scientists think that "the paper which could not be reproduced is wrong content", it seems that many think that the published paper is worthy of trust. This is probably because many scientists have experienced in the past that "experiments can not be reproduced" in the past.
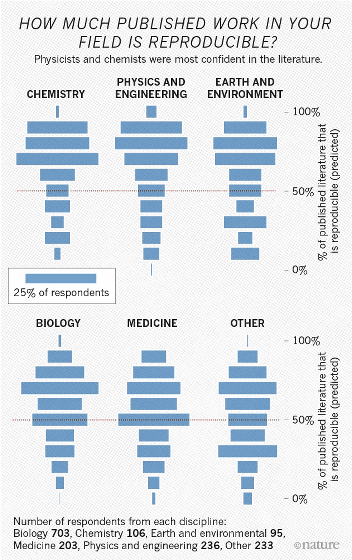
In addition, 73% of the respondents who responded to this survey said they believe that at least 50% of the papers published in scientific journals published in their research field are worthy of trust. The area of chemistry and physics & engineering was the one that puts the most reliance on the published research content.
However, the definition of what "reproducibility" should be in contemporary science is not clear. In order to preserve the accuracy of science, it may be that the time has come for an agreement on what to reproduce and what should be reproducedJohns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health"Said Professor Arturo Casa Debal, a microbiologist at the University of California.
Also, the fact that "the experiment of another scientist could not be reproduced" can be accepted as an indication of my incompetence, and because there is a possibility of leaking out his research content, There was only 20% of the people who reported to the research group of the head family that it could not be reproduced, which is also one of the problems.
And, if there are few people who are trying to publish research to reproduce the research that has already been done in the first place, and moreover, the result is that it can not be reproduced, the publisher who wants to avoid negative content will write a paper It is an obstacle to the reproducibility of science that it does not want to be posted.
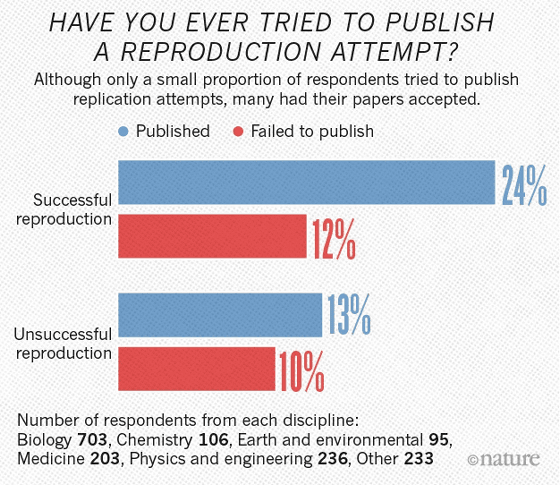
The probability of posting of researchers who tried to publish reproduction research in scientific journals is as follows. Among the successfully reproduced studies, the percentage posted in scientific journals was 24%, and the rate of refusal to post was 12%. On the other hand, in the case of research that failed to reproduce, the probability of being posted was low, which was only 13%.
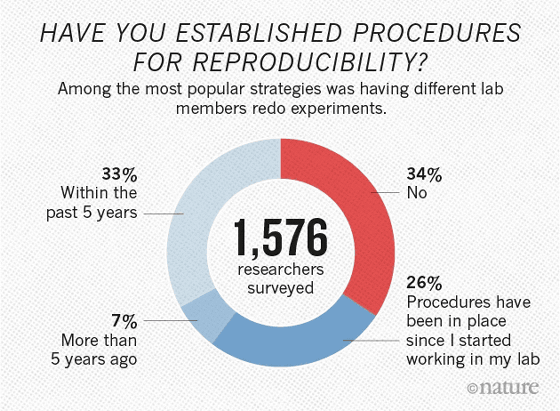
Among the respondents, one-third of all respondents replied that "concrete efforts to promote the reproduction of experiments in laboratories in the past five years was done" , The most reluctant to the effort was 24% in the field of physics & engineering, and 41% in the field of pharmacy that was aggressive. Among those mentioned as concrete contents of the initiative, the most frequent case was "to conduct experiments on your own once again" and "to ask someone in the laboratory to reproduce".
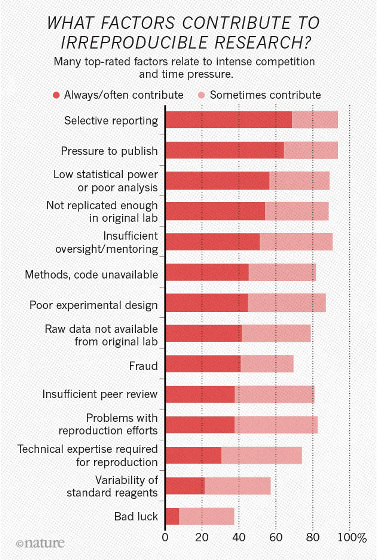
With respect to the question item "What is the obstacle in the reproduction of research, more than 60% of the respondents said that" two types of "selective reporting" and "pressure on publication" are always / often become obstacles It is selected as being ". In addition, more than half of the respondents cited the laboratory's lack of verification, insufficient supervision, low detection ability, etc. as "always / often obstructive", and the technical difficulty in reproduction A few people thought that it was a point.
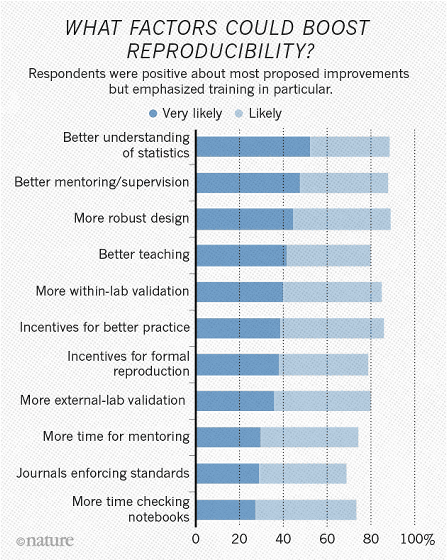
So what is necessary to improve the reproduction process? In response to the questionnaire, the most frequently chosen answers are "to better understand statistical data", "to improve guidance and supervision", "to make the experimental plan more robust", more than 90% I agree with these proposals. The idea of setting incentives and improving the eyes of the publisher's checks has become less popular as an idea to improve the reproduction process.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log