A method to make a battery with almost infinite life is developed

by
MIT and Samsung have announced that they have developed a solid electrolyte to replace the liquid electrolyte used in today's lithium-ion batteries. This has been shown to extend battery life to 'nearly infinite', improve safety, and improve cold resistance.
Samsung, MIT find way to make batteries with'indefinite' lifetime – The Korea Times
http://www.koreatimesus.com/samsung-mit-find-way-to-make-batteries-with-indefinite-lifetime/
Going solid-state could make batteries safer and longer-lasting | MIT News
http://newsoffice.mit.edu/2015/solid-state-rechargeable-batteries-safer-longer-lasting-0817
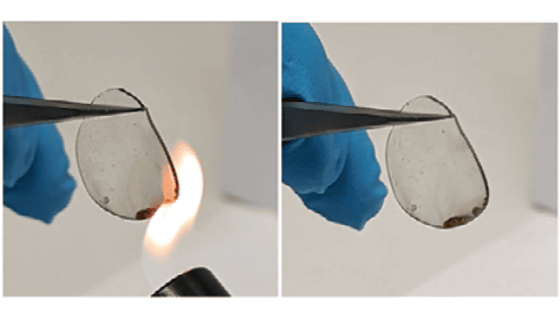
Lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used batteries, use an electrolytic solution in which a lithium salt is dissolved in an organic solvent such as ethylene carbonate (ethylene carbonate) or diethyl carbonate as the electrolyte, but this organic solvent is flammable. , Ignition accidents have occurred.
Therefore, what was needed was a 'solid electrolyte' that does not have a risk of ignition, but in general, solid electrolytes have the problem that the charge / discharge rate is slow because the conduction characteristics of lithium ions are not as good as those of organic solvent systems. ..
This time, MIT and Samsung have overcome this point that 'solid electrolytes do not have better conduction characteristics than electrolytes' with superionic lithium-ion conductors, which are compounds of lithium, germanium, phosphorus, and sulfur. 'It has been thought that solids do not have sufficient conduction properties, but that paradigm has been overturned,' said Gerbrand Cede, a visiting professor at MIT, who specializes in materials science and engineering.
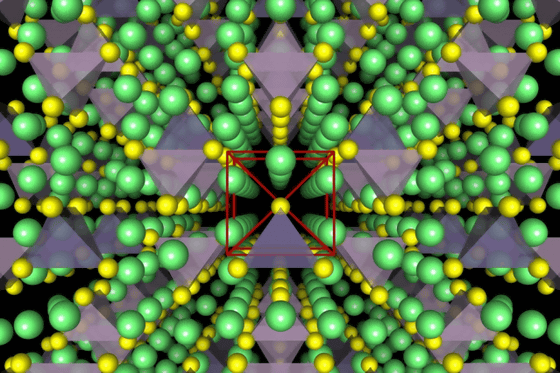
This is a diagram of the crystal structure of a superionic conductor. The lithium atom is drawn in green, the sulfur atom is yellow, the PS4 tetrahedron is purple, and the GeS4 tetrahedron is blue.
by MIT
As mentioned above, the accident that ignites a lithium-ion battery is not because lithium is flammable, but because the organic solvent is flammable. By stopping the use of electrolytes and using solid electrolytes, the risk of ignition is eliminated.
Furthermore, with conventional lithium-ion batteries, the life cycle is about 500 to 1200 times in the JIS test. Although it does not match the number of charges and discharges, solid electrolytes increase the cycle to hundreds of thousands, so they can be used almost endlessly.
In addition, as a side effect, when the electrolyte is used, the performance deteriorates when it gets cold at about -20 ℉ (-28.8 ℃), but if it is a solid electrolyte, it is the original regardless of the cold. It is possible to demonstrate the performance. In addition, the output density will be improved by 20 to 30% compared to the conventional model.
If it is put into practical use, there may be no need to worry that 'if you were charging the battery of your smartphone or laptop while you were sleeping, it would suddenly explode.'
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by logc_nt