A clear image of the `` Tarantula Nebula '' taken by the James Webb Space Telescope will be released, a clue to the mystery of `` noon in the universe ''

The
A Cosmic Tarantula, Caught by NASA's Webb | NASA
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2022/a-cosmic-tarantula-caught-by-nasa-s-webb
Stunning Webb View of Tarantula Nebula Captures Details Never Seen Before : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/stunning-webb-view-of-tarantula-nebula-captures-details-never-seen-before
A nebula called `` 30 Doradus '' at a distance of about 160,000 light years from the earth is also called `` Tarantula Nebula '' because its complex internal structure looks like a tarantula. The Tarantula Nebula is a very bright celestial object and is said to be the largest and most active star-forming region in the local group of galaxies to which the Milky Way Galaxy belongs.
The following image is a composite of images taken by the VLT and VISTA telescopes built by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in the past. It certainly looks like a hairy tarantula.

by ESO, ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/Wong et al.
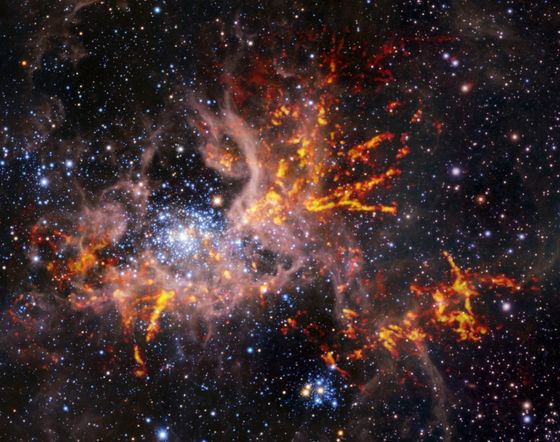
On September 6, 2022, NASA released a clear image of the Tarantula Nebula taken with the James Webb Space Telescope. Below is an image taken with the NIRCam (near infrared camera) mounted on the James Webb Space Telescope. As a result of being able to see a large number of stars that could not be confirmed with conventional observation equipment, there is a young star cluster (the part that shines pale blue) in the center of the Tarantula Nebula, and the

The image below is a longer infrared wavelength captured by MIRI (mid-infrared observation device). In the MIRI image, hot stars are no longer visible, and cold gas and dust are clearly visible.
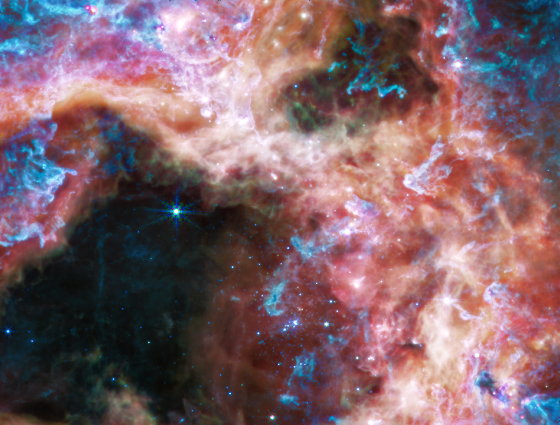

One reason the Tarantula Nebula is of interest to astronomers is that it has a chemical composition similar to that of celestial bodies during a period called ' cosmic noon .' Cosmic noon is a term that refers to the period of rapid growth of galaxies about 2 to 3 billion years after the Big Bang. During this period, a huge star-forming region had a different chemical composition from the Milky Way galaxy where Earth resides. I have.
However, although the Tarantula Nebula is only about 160,000 light years away from the earth, it has a chemical composition similar to the star-forming region in the midday of the universe. Therefore, analyzing the Tarantula Nebula is expected to provide important clues about what was happening at midday in space.
'Mankind has observed stars for thousands of years, but there are still many mysteries about the process of star formation, many of which lie behind the thick nebulae where stars form,' NASA said in an official statement. The James Webb Space Telescope is already beginning to reveal a never-before-seen view of the universe. , This is just the first step in rewriting the story of how stars are born.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik