Chinese researchers develop quantum computer-based method to crack RSA encryption

Wang Chao and his colleagues at Shanghai University have announced that they have developed a method to break RSA encryption, a cryptography whose security is based on the difficulty of prime factorization, by using quantum computers.
Fundamentals of D-Wave Advantage's quantum extinguishing public information, offensive arithmetic research
(PDF file)
Chinese researchers break RSA encryption with a quantum computer | CSO Online
https://www.csoonline.com/article/3562701/chinese-researchers-break-rsa-encryption-with-a-quantum-computer.html
Chinese Scientists Report Using Quantum Computer to Hack Military-grade Encryption
https://thequantuminsider.com/2024/10/11/chinese-scientists-report-using-quantum-computer-to-hack-military-grade-encryption/
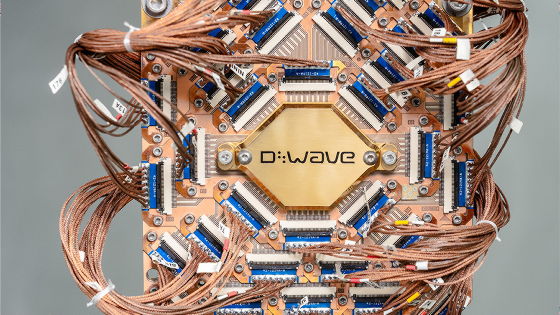
According to a peer-reviewed paper published in the Chinese Journal of Computers, Wang and his colleagues used the D-Wave Advantage quantum computer from Canada-based D-Wave Systems to integrate classical algorithms, quantum annealing and other techniques to successfully optimize the system for several encryption algorithms.
It has been thought that quantum computers might eventually be able to crack existing encryption, but this research suggests that such a threat could come much sooner than expected.

According to experts, the significance of Wang's research lies in 'combining quantum annealing algorithms with traditional mathematical approaches to create a new computational architecture and presenting encryption problems as binomial optimization problems suitable for quantum computers.'
The algorithms that Wang and his colleagues looked at are the basis of systems widely deployed in military and financial encryption protocols, some of which are considered 'the most secure currently available.' But their findings suggest that quantum computers may soon pose a threat to their security.
Wang and his colleagues studied two types of quantum annealing-based RSA public key attack algorithms. The first is a model that combines the mathematical techniques of cryptographic attacks to convert them into an optimization problem or exponential space search problem, making it possible to solve them using existing methods such as
The second is called a quantum annealing algorithm fusion cryptography attack. Wang et al. optimized the approximate nearest neighbor algorithm by combining quantum annealing and classical algorithms, and succeeded in prime factorizing a 50-bit integer, 845546611823483 = 40052303 × 21111061, using 10 logical qubits and 16 physical qubits. Wang et al. took the approach of randomly selecting RSA integer factorization within the range of 4 to 50 bits, which was also a significant demonstration experiment to prove the universality and scalability of the algorithm.

A major technological breakthrough would be required to crack the 2048-bit or larger keys currently in use at the time of writing, but Wang et al.'s method may also be applicable to factoring RSA integers of 64 bits or more in the future. 'Even data that is encrypted today could be stolen in anticipation of future decryption, putting such data at risk. As quantum attacks become a reality, organizations need to rethink how they secure their data,' they warned.
Related Posts: