Research using AI reveals that Raphael's painting may have been a collaborative work

When we used AI to investigate the famous work ``Madonna of the Roses'' by Raphael, an Italian painter representing the Renaissance period, we found that although most of it was done by Raphael, there were some additions by people other than Raphael. It became clear.
Deep transfer learning for visual analysis and attribution of paintings by Raphael | Heritage Science | Full Text
AI study shows Raphael painting was not entirely the master's work
The research was carried out by a team of experts from the University of Nottingham, University of Bradford and Stanford University.
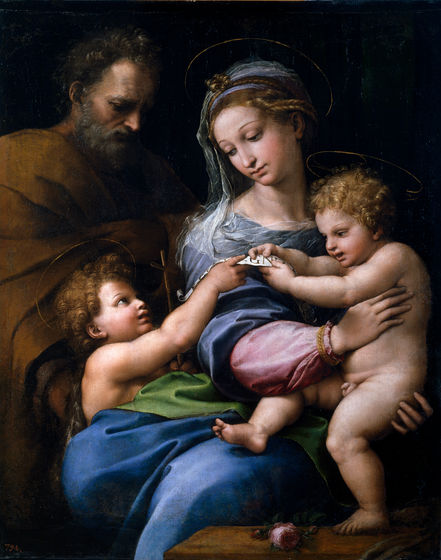
``Madonna of the Roses'' is a painting stored in the Prado Museum in Madrid, Spain, and Raphael researcher Professor Jurg Mayer za Capellen and others believe that it is possible that his disciple Giulio Romano contributed to it. It has also been suggested that the rose and the area below it were painted by someone other than Raphael.

Professor Hassan Ugair, director of the Center for Visual Computing and Intelligent Systems at the University of Bradford, has developed an algorithm that can identify Raphael's works with 98% accuracy.
When ``Madonna of Roses'' was checked using this algorithm, it was confirmed that the rose and the part below it, which had been rumored to have been drawn by someone else, were actually drawn by Raphael.
However, on the other hand, it turns out that there is a high possibility that the part of St. Joseph depicted was painted by someone other than Raphael.
Professor Emeritus Howell Edwards from the University of Bradford said: ``When we checked the works with our AI, it was clear that the Virgin Mary, the Infant Christ, and St. John the Baptist were painted by Raphael, while St. Joseph was painted by Raphael. Instead, it has been conclusively proven that it was clearly painted by someone else, and Professor Tsa Kapelen and others believe it was by Romano.
Related Posts:







