Research results of shock that life activity can be recovered from suffocation by taking in microorganisms into the body and photosynthesizing will be announced
Oxygen is essential for the brain, which supports the vital activities of vertebrates, so organisms that are suffocated in a severely hypoxic environment will cease neural activity. In
Green oxygen power plants in the brain rescue neuronal activity
https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042 (21) 01126-3
Injecting Algae Into Suffocated Tadpoles Brings Their Brain Cells Back to Life
https://www.sciencealert.com/injecting-algae-into-the-brains-of-suffocating-tadpoles-keeps-their-neurons-alive
The oxygen needed by vertebrates is taken up primarily from the lungs, ella and skin. Especially for brain activity, a certain amount of oxygen needs to be continuously supplied. Therefore, in a low oxygen environment such as diving into the deep sea or flying at high altitude, keeping the oxygen supply is an important issue.
One of the means to generate oxygen is photosynthesis by green plants, and it has been reported that the natural symbiosis between organisms that actually perform photosynthesis and marine animals. The experiment conducted by Ludwig Maximilian University this time is to inject algae that perform photosynthesis into the body of Xenopus tadpoles and illuminate it strongly to generate photosynthesis in the body and supply oxygen to the brain. ..
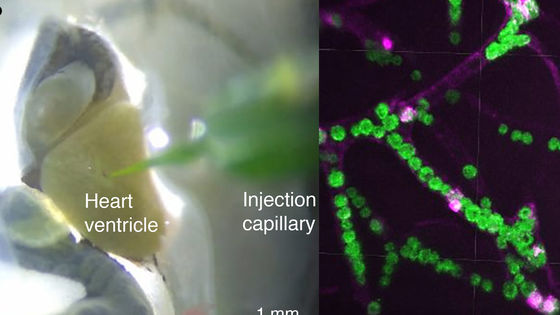
When you inject green plankton into a translucent tadpole as shown on the left of the image below, you can see that the tadpole is dyed green as shown on the center and right of the image.
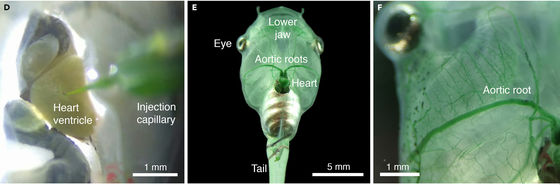
Also, if you magnify the body tissue with a microscope, you can see that green plankton that can photosynthesize is diffused to the microvessels of tadpoles.
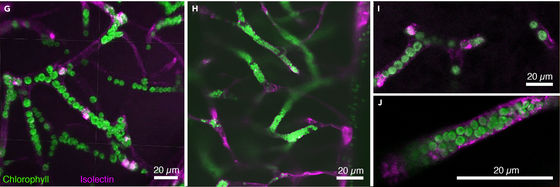
Click on the image below to watch a movie of algae plankton injected into the heart spreading through blood vessels.
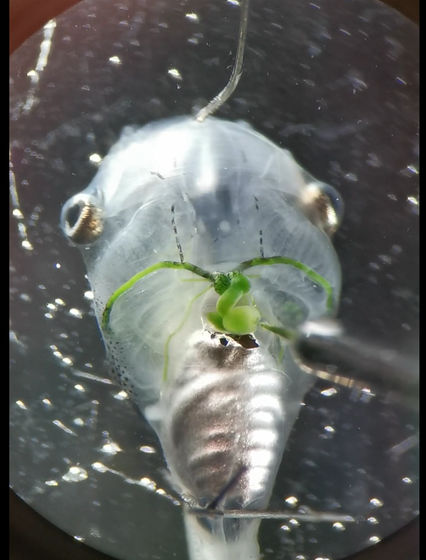

In the experiment, after injecting algae plankton into tadpoles, a part of the nervous system was isolated to disable normal self-reliant neural activity. As a result, it has been reported that light-irradiated plankton in the body produces oxygen, which acts as a substitute for brain activity.
The image below shows how neural activity responded to alternating light and dark conditions. As shown in the red frame, you can see that after a while when the light is applied, a reaction occurs in the nerve activity, and after the light goes out and a certain period of time elapses, the activity stops again.
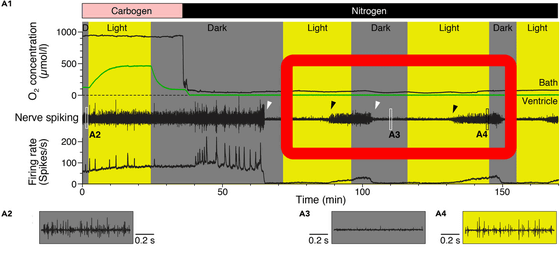
The research shows that photosynthetic microbes can show the ability of organisms to save brain activity, the researchers say. It is expected that this will also provide a means to increase oxygen levels as a method of helping pathological disorders in the future.
However, this experiment only proved the principle that the irradiated light can pass through the skin and act on the microorganisms in the body because it is a transparent tadpole, and the microorganisms can supply oxygen. In addition, while the experimental results are very innovative, the research team also acknowledges harmful risks such as long-term immune response by injecting microorganisms into the body, and it can be expanded to longer-term experiments and application fields. It says it is necessary.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1e_dh