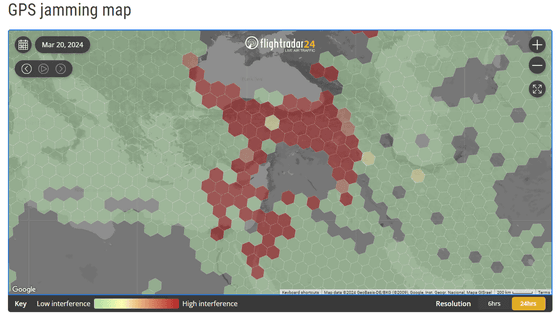
'GPS Test' review that allows you to check the type and accuracy of satellites used by Android devices
GPSTest-Google Play app
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.android.gpstest
gps-test-app-definition.pdf
(PDF file) https://www.euspa.europa.eu/simplecount_pdf/tracker?file=gps-test-app-definition.pdf
First, install GPS Test from the Google Play store.
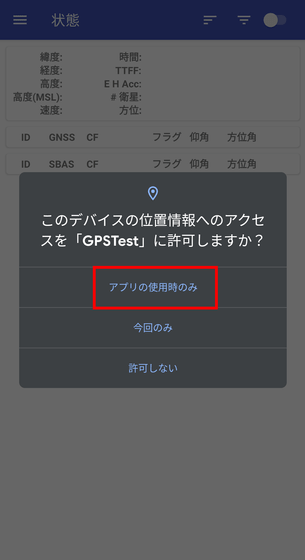
When you open GPSTest, you will be asked to access the location information, so this time select 'Only when using the app'.
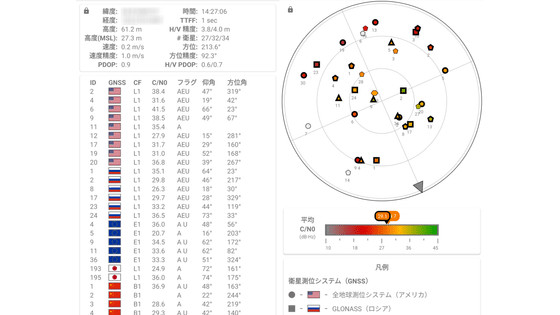
Then, the measurement of location information will start automatically first. The home screen of GPS Test after measurement looks like this. Various measured values are displayed at the top, and satellite information is displayed at the bottom.
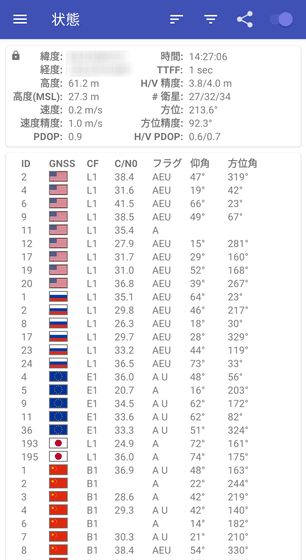
The information at the top represents the following:
・ Latitude: Latitude of the current location of the terminal
・ Longitude: Longitude of the current location of the terminal
-Altitude: The altitude of the terminal
-Altitude (MSL): Altitude based on the average sea level (MSL) of the terminal's current location
・ Speed: Current speed of the terminal
-Speed accuracy: Confidence interval with 68% reliability of terminal speed. For example, when the speed is 5.0 m / s and the speed accuracy is 1.0 m / s, if you measure 100 times, you will get measurement results in the range of 4.0 m / s to 6.0 m / s 68 times.
・ PDOP: PDOP (Position accuracy reduction rate)
Positioning accuracy is best when PDOP is 1.0, and positioning accuracy decreases as the value increases.
-Time: The current time of the terminal's current location obtained from GNSS
・ TTFF: Time from the start of GPSTest to the acquisition of the first positioning
-H / V accuracy: Confidence interval of 68% reliability in the horizontal and vertical directions with respect to latitude and longitude.
-# Satellite: Number of satellites used / Number of satellites with sufficient signal strength / Number of satellites recognized by the terminal
・ Direction: The direction of the terminal
-Orientation accuracy: Confidence interval of 68% reliability of the orientation of the terminal.
・ H / V PDOP: Horizontal / vertical position accuracy reduction rate
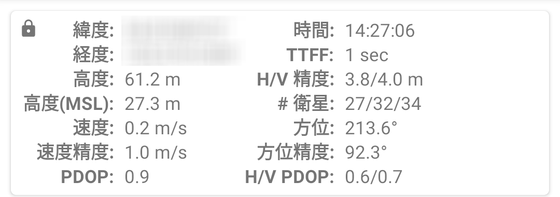
The information displayed at the bottom represents the following:
・ ID: PRN number assigned to each satellite
・ GNSS: GPS for the American flag, GLONASS for the Russian flag, etc.
・ CF: Frequency band of satellite positioning signal
・ C / N0: Carrier-to-noise ratio
-Flag: 'E' if the satellite has broadcast calendar data, 'A' if it has precision calendar data, if the satellite was used for the latest positioning Notated as 'U'
・ Elevation angle
・ Azimuth
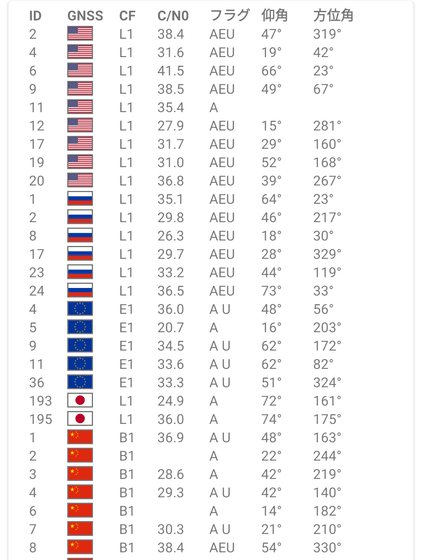
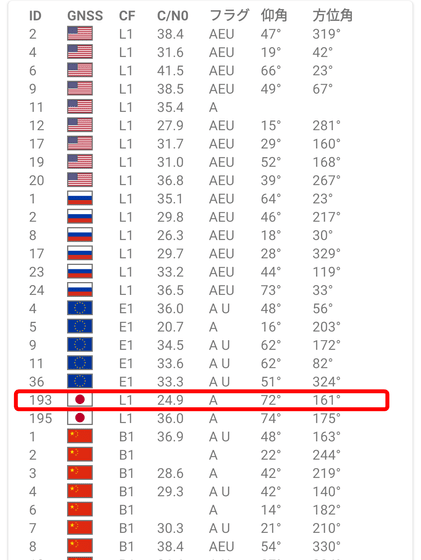
For example, the PRN number 193 displayed this time is the first quasi-zenith satellite system 'MICHIBIKI', which is one of the satellites that make up QZSS. The positioning signal frequency is L1 (1575.42MHz), and the carrier-to-noise ratio is 24.9. Since it has precision calendar data, it is written as 'A', and since it was not used in this positioning, there is no notation of 'U'. The elevation angle is 72 degrees and the azimuth angle is 161 degrees.
The functions that can be used by tapping the four icons lined up at the top of the screen are 'Sort' from the left ...
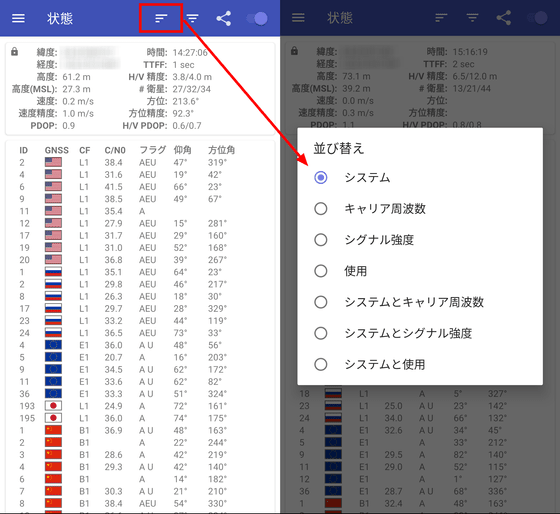
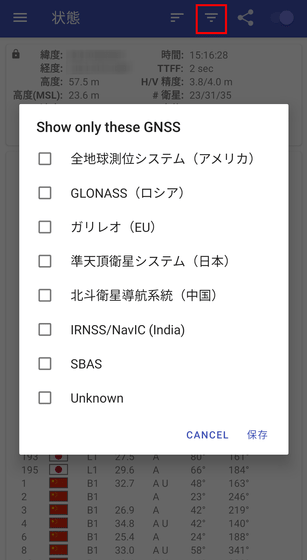
Switching the GNSS to be displayed.
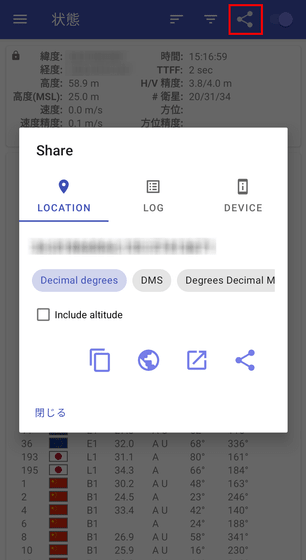
Sharing of current location information.
Switching between starting and stopping positioning.

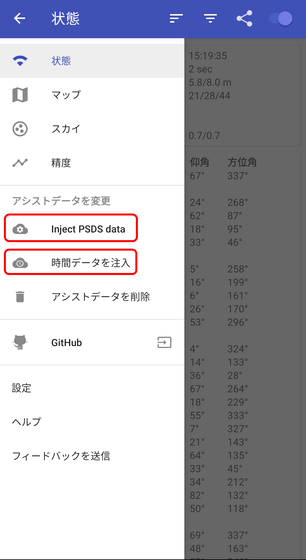
Tap the hamburger menu on the upper left to display the following information.
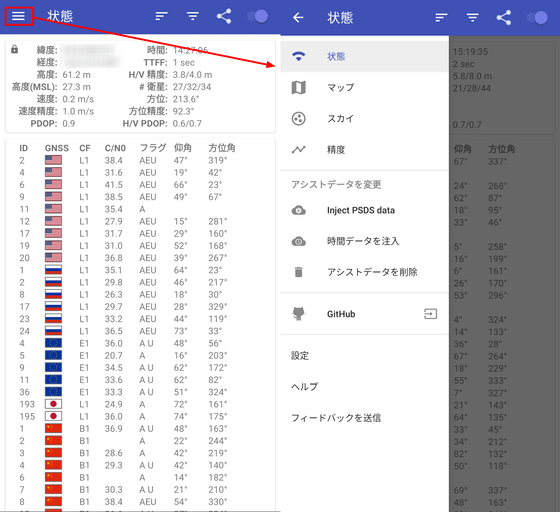
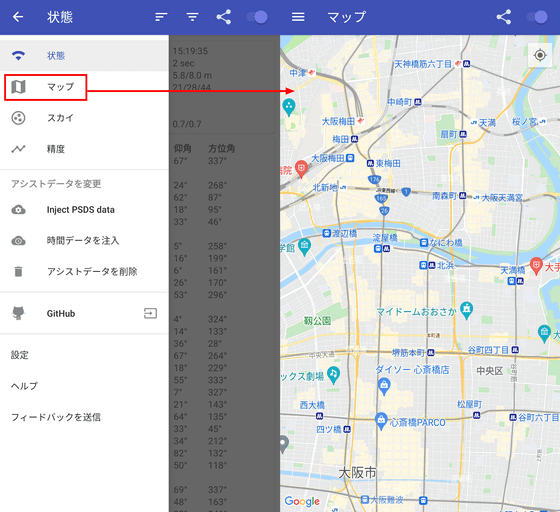
As the name suggests, 'Map' displays a map ...
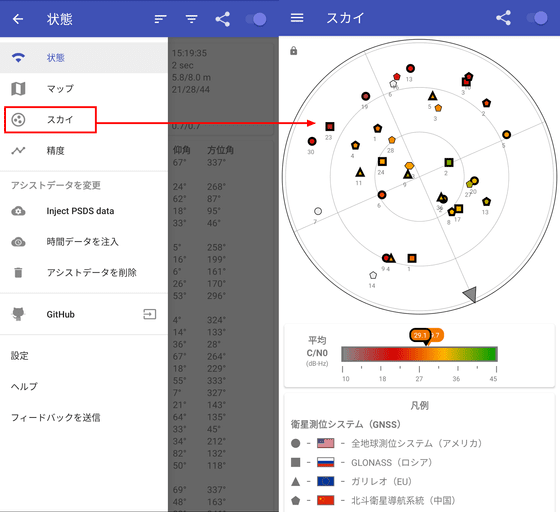
'Sky' can confirm the direction in which each GNSS exists.
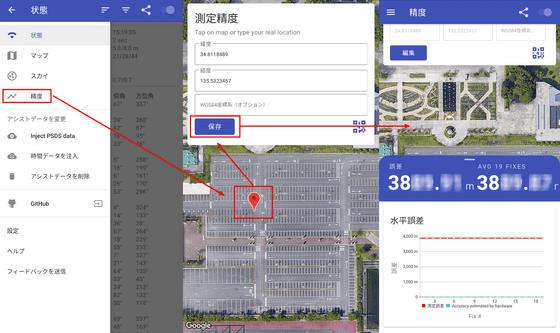
You can check the measurement accuracy in 'Accuracy'. If you tap your current location on the map and then press 'Save', you can check the error between the location information obtained by positioning and the actual current location.
'Inject PSDS Data' is a function to add information obtained from Wi-Fi or mobile line to positioning, and 'Inject time data' is a function to add time information from
By using GPSTest, you can check how many satellites your Android device uses to measure location information and how accurate it is.
Related Posts: