Research results show that dinosaurs have been on the path of decline even before the asteroid collision

Dinosaur biodiversity declined well before the asteroid impact, influenced by ecological and environmental pressures | Nature Communications
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23754-0
Dinosaurs were in decline before the end, according to new study
https://phys.org/news/2021-06-dinosaurs-decline.html
Large Dinosaurs Were Prone to Extinction Way Before The Asteroid, New Study Argues
https://www.sciencealert.com/non-avian-dinosaurs-were-in-decline-before-extinction-asteroid-hit-earth
About 66 million years ago, a giant asteroid that entered the atmosphere at 60 times the speed of sound collided with the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. The collision released the energy of billions of nuclear weapons, and the asteroid itself quickly evaporated, burning everything that exists in a radius of about 1500 km.
After that, debris with a mass equivalent to 60 times that of an asteroid was scattered in outer space, a magnitude 11 class impact was transmitted to the entire earth , a volcanic eruption of 30,000 years continued in the Indian subcontinent , and a tsunami with a height of 1000 m occurred. It seems that an incredible catastrophe, such as an outbreak, struck animals and plants. Then, the rocks evaporated due to the collision and the soot generated by the forest fire blocked the sunlight, and the large amount of sulfur evaporated combined with the oxygen in the air, and the sulfate aerosol generated cooled the earth, resulting in a large scale. It is believed that a large number of organisms have become extinct due to various climate change.

Generally, there is a perception that the dinosaurs that had prospered until then suddenly became extinct due to the collision of asteroids, but paleobiologists said, 'Before the collision of asteroids, the sea surface associated with continental drift on the Earth at the end of the
In 2016, a systematic study was published stating that dinosaurs had declined before the asteroid collision, but this is a fossil record-based analysis and is controversial due to its high uncertainty. It is said that it has become a target. Therefore, international research teams in France, the United Kingdom, and Canada used a model based on Bayesian statistics to consider fossil data bias and dating uncertainty for over 1600 dinosaur fossils of the Cretaceous period. Speciation and extinction rate were evaluated after putting it in.
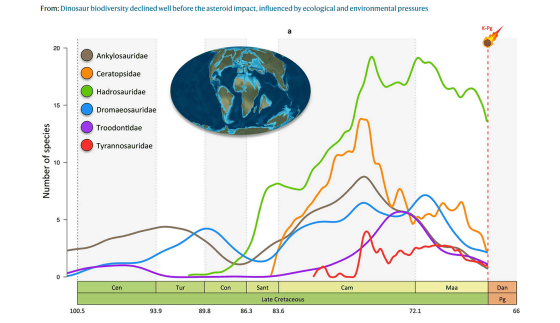
This is the graph showing the results of the analysis. The vertical axis shows the type of dinosaur and the horizontal axis shows the time. Brown is ' Ankylosauridae ', orange is ' Ceratopsidae ', green is ' Hadrosauridae ', and blue is blue. ' Dromaeosauridae ' is represented by purple, ' Troodonitdae ' is represented by purple, and ' Tyrannosauridae' is represented by red. It can be seen that the diversity of dinosaurs has gradually decreased since about 10 million years ago, when the K-Pg boundary on the far right, which indicates the collision of asteroids, was reached.
In the graph below, the left shows the speciation rate (blue) and the extinction rate (red) of the whole dinosaur, and the right shows the diversity rate of the whole dinosaur, both of which show the time on the horizontal axis. I will. Looking at both graphs, we can see that the extinction rate of dinosaurs has increased and the diversity has decreased even before the asteroids collided.
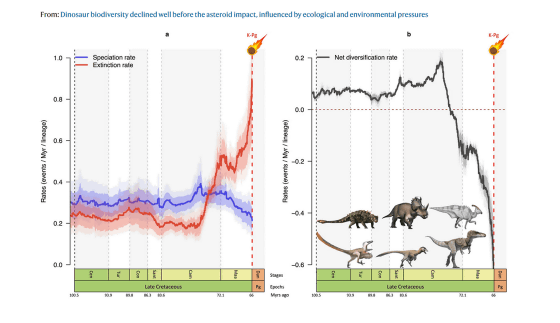
According to the research team, the diversity of dinosaurs began to decline around 77 million years ago, 10 million years before the asteroids collided. 'We examined the six most prosperous dinosaur families throughout the Cretaceous from 150 to 66 million years ago,' said Fabien Condamine, a member of the Institute for Evolutionary Sciences at the University of Montpellier, France. '76 million years ago, they suddenly went down. The extinction rate increased and the incidence of new species could decrease.'
The decline of dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous may be due to the cooling of the earth, and the research team wrote in a treatise, 'This result was favorable for dinosaur diversification in the warm season, but in the cold season. Suggests that it has promoted extinction. ' In particular, large dinosaurs needed a warm climate to stabilize their body temperature, so they may have been susceptible to cooling. In addition, when the sex of the embryo changes depending on the temperature like a sea turtle, it is hypothesized that the lower temperature causes a bias in the sex of the offspring, resulting in loss of diversity.
In addition, looking at how the dinosaur ecosystem declined, it became clear that herbivorous dinosaurs tended to become extinct first. Since herbivorous dinosaurs form the lower layer of the food chain, it seems that the disappearance of herbivorous dinosaurs may have affected the carnivorous dinosaurs located above it.
'This was an important moment in the evolution of living things. The Earth has been dominated by dinosaurs for over 160 million years, and as they declined, another group, including mammals, became dominated. Many of the dinosaurs were huge, so it would have been hard to notice that there were small furry mammals at their feet, but today the number of mammals began to grow before the dinosaurs went extinct, and today after the asteroids collided. I got the chance to create a new ecosystem like this. '
Related Posts:







