What drugs could be a game changer in the fight against the new coronavirus?
Since November 2020, the number of people infected with the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) has been increasing in Japan, and the British media has announced the existence of a drug that can be a
The breakthrough medicines that could change the course of Covid | Coronavirus | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/dec/27/the-breakthough-medicines-that-could-change-the-course-of-covid
In June 2020, a research team at Oxford University in the United Kingdom found that the globally widely used steroidal anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone could significantly reduce the mortality rate of critically ill patients with COVID-19. Showed that there is.
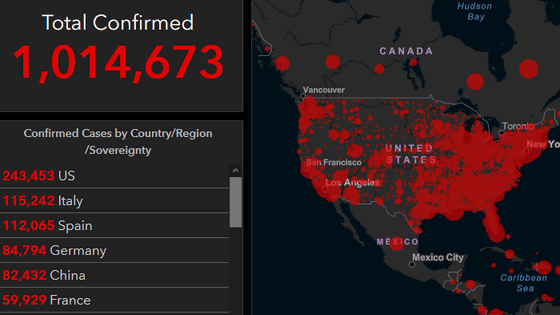
It is suggested that cheap anti-inflammatory drugs may dramatically reduce the mortality rate of severely ill patients with the new coronavirus --GIGAZINE
Dexamethasone has been shown to be effective in the world's largestrandomized clinical trial, Recovery, for the treatment of COVID-19. Martin Landley, a professor at Oxford University, said that the discovery that dexamethasone was effective in critically ill patients with COVID-19 saved about 650,000 lives by the time the article was written. I'm estimating. 'In the UK alone, dexamethasone has already saved more than 12,000 lives,' said Professor Landley.
Professor Landley-led recovery is investigating other drugs that can help treat COVID-19 besides dexamethasone, and may find other promising drugs in the coming weeks. .. Particularly effective are ' plasma collected from COVID-19 patients', 'Regeneron monoclonal antibody' used to treat President Trump, anti-inflammatory drugs tocilizumab and colchicine , and aspirin. 'Combination'. These treatments are being piloted in tens of thousands of COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the United Kingdom, with initial trial results expected to be revealed around January-February 2021.

The randomized clinical trial 'Recovery' is a project launched by Professor Randley in collaboration with epidemiologist Peter Hobby, who is studying emerging infectious diseases at Oxford University. When the pandemic of the new coronavirus occurred, doctors working in the field were looking for a cure for COVID-19, and the two were clinical trials of 'more effective' of multiple treatments. I thought I needed to find it inside, so I started recovery. First of all, it seems that it took only '9 days' to decide the specifications related to recovery and register the subjects to participate in recovery, but it usually takes 9 months for such a process. ..
'By conducting randomized clinical trials like recovery on real patients, we can see which treatments actually work. Finding out which patients will benefit most. If possible, it is possible to identify whether young people and old people have weakened immunity in the same way. It is possible to find out that fact because it is a test involving thousands of people. We can do it, 'he said, claiming that the large number of patients involved in recovery has made it easier to find effective treatments for COVID-19.
So far, four drugs have been used for recovery: azithromycin , an antibiotic, ropinavir ritonavir , an antiviral drug, hydroxychloroquine , a treatment for malaria and rheumatoid diseases, and dexamethasone. The effect has been verified. As a result, it has been clarified that other than dexamethasone is ineffective as a therapeutic drug for COVID-19.
Dexamethasone was the only effective therapeutic agent, but as mentioned above, it has saved the lives of an estimated 650,000 critically ill COVID-19 patients, so the usefulness of recovery is clear. 'When we started recovery, we looked at cheap and widely available medicines and found that dexamethasone was effective against COVID-19, but the medicines we are currently testing are treatments. Because each is expensive, costing hundreds of pounds (tens of thousands of yen), it is not possible to verify that these treatments are 'really effective for patients' before they are rolled out on a large scale. It's a necessary act, 'he said, arguing that recovery will play a more important role in the future.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii