What is the evolution of how to obtain the 'geothermal' that is expected to generate large amounts of renewable energy?

Research on renewable energies such as solar power and wind power is one of the fields for which further development is desired as a way to obtain the energy required for human society while protecting the global environment. Vox, a news media, summarizes the development of a system for obtaining 'geothermal' energy, which is expected to be a major energy source among renewable energies.
Geothermal energy is poised for a breakout --Vox
Geothermal energy is the energy obtained by utilizing the heat generated by magma above 5000 ° C, which is underground about 5000 km deeper than the earth. Geothermal energy is considered to be a type of renewable energy, and AltaRock Energy, a project to promote geothermal energy development at the Advanced Energy Research Planning Bureau in the United States, said, 'Only 0.1% of the amount of heat that the earth has, human beings need it for 2 million years. It can supply total energy. '
Geothermal energy has been used by humans for a long time, and even before the advent of geothermal power generation, hot water at around 100 ° C, which was heated by geothermal energy and sprang up on the surface of the earth, has been used as energy for cooking and heating. With the development of technology, it has become possible to generate electricity with geothermal energy, but the amount of heat generated by high-temperature steam is required to convert it into electricity. In conventional geothermal power plants, water is separated from the high-temperature steam generated by geothermal heat, and steam is used to operate a turbine to generate electricity.

However, Vox reporter David Robert said, 'There are some problems with traditional geothermal power generation.' Mr. Robert points out that the problem is that 'there is a bias in areas where high-temperature steam can be abundantly obtained.' Areas such as Iceland and California are blessed with geothermal areas such as huge fumaroles on the surface of the earth, but it is difficult to draw heat from underground due to the influence of geology and areas where the heat source that can be used for energy is deep underground. It is said that the area occupies more.
'At least with traditional technology, most of the areas that excel in geothermal energy have been dug up, especially resource-dependent power generation, such as water vapor, which makes it difficult to standardize and scale up. Geothermal energy development has lagging behind other renewable energies. '
Therefore, the development of geothermal energy utilization methods that are different from conventional power generation methods has been promoted. For example, geothermal power generation systems called
The United States Department of Energy said, 'Compared to the total annual US energy consumption of 1754 terawatts required for residential and commercial facilities, the energy obtained from EGS is theoretically at least 8500 years or more for all US home and commercial facilities. That's enough to warm up. '

Robert also cites a system called 'Eavor-Loop' planned by Canadian technology company
Water flows in the direction of A → B → C → D → E in the pipe of Eavor-Loop. The pipe is a loop, and water circulates by taking advantage of the fact that colder ones tend to sink down. The cold water shown in blue sinks and the hot water shown in red rises, so water can be circulated naturally without the need for a pump. At the time of writing the article, Eavor-Loop can get heat around 150 ℃.
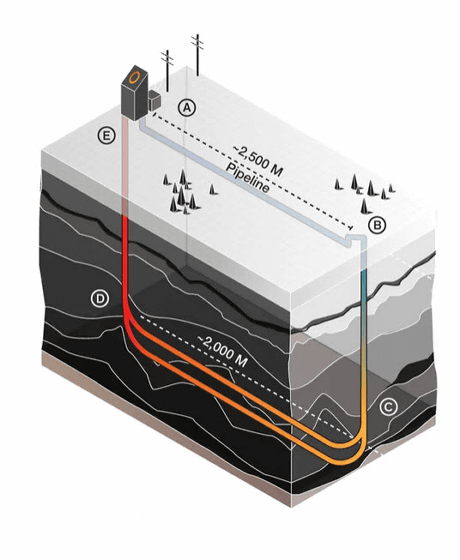
In addition, the 'Eavor-Lite' project, which is an extension of Eavor-Loop, is also underway. Eavor-Lite is an extension of Eavor-Loop, and you can see what kind of shape it is by watching the following movie.
Eavor Lite to James Joyce Animation-YouTube
Eavor-Lite is shaped like an Eavor-Loop pipe folded in half ...
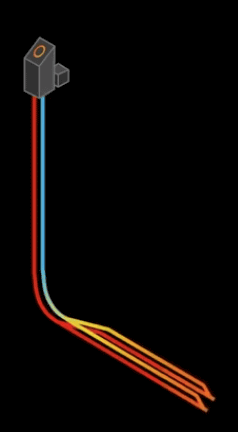
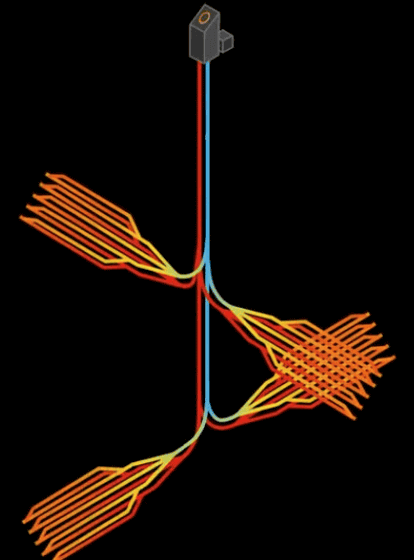
The surface area has been further increased by increasing the number of horizontal pipes in all directions. Eavor-Lite is planned to be installed in 3 to 4 locations in Canada, and it is planned to be installed in Germany, France, and Japan after 2021.
'The clean energy industry continues to grow, and the decade after 2020 will be even more vigorous than ever before,' said Robert. 'The world's fully renewable power supply. The vision is more and more within reach. '
Related Posts:







