'Plants that shine in the dark' are made by gene recombination technology using the substances that the plants themselves have

Plants with genetically encoded autoluminescence | Nature Biotechnology
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-020-0500-9
Scientists Engineer Gorgeous Glowing Plants That Shine Bright Their Entire Life Cycle
https://www.sciencealert.com/gorgeously-glowing-plants-shine-bright-throughout-their-life-cycle
Bioluminescence is a phenomenon that emits light by its own energy under the conditions there is no external light, Hikarigoke and Chromophyton rosanoffii as, those shiny and reflects a slight light coming from the outside is not included in the bioluminescence Hmm. Although attempts have been made to illuminate plants by genetic engineering technology for a long time, the research team is more than the luminescent plants developed so far without administering chemicals to maintain luminescence from the outside. We have created a plant that emits light for a long time.
The state of the plant that actually emits light in the dark can be seen in the following movie.
Timelapse video of incredible glowing plants growing .-- YouTube
The plant that has been developed this time is fantastically glowing in the dark. You can also see the shape of the veins by the light and darkness of the light.
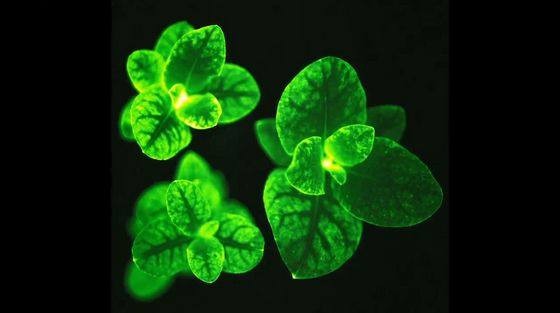
The tip of the plant seems to be brighter, and the flowers are especially bright.
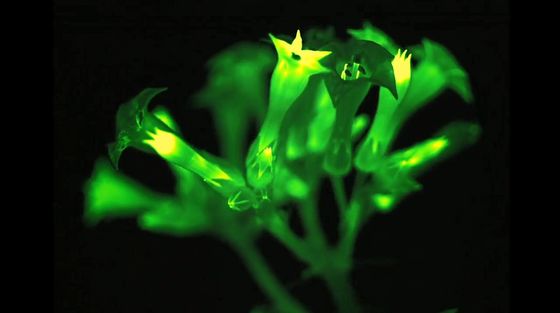
In the previous research, it seems that gene manipulation was performed using DNA such as bioluminescent bacteria, but although bacterial genes can target self-luminance by targeting the
Therefore, this time, it was said that genetic manipulation was performed using DNA of bioluminescent fungus instead of bacteria. A 2018 study published by almost the same members of the research team found that a chemical called caffeic acid is involved in the luminescence of fungi.
Inside the bioluminescent fungus, a total of four enzymes act to biosynthesize a substance called luciferin, which is the source of bioluminescence, from caffeic acid. Of these four enzymes, the first and second enzymes convert caffeic acid to luciferin, the third enzyme oxidizes luciferin to produce photons , and the fourth enzyme leaves the remaining molecule. It has the role of converting to caffeic acid again.
Importantly, caffeic acid is an important intermediate in lignin biosynthesis that provides rigidity and strength to plant cell walls and is present in all plants. The researchers wondered if genetic engineering could allocate some of the caffeic acid in the plant to luciferin biosynthesis, causing the plant to glow. Therefore, the research team reports that after cultivating by combining four bioluminescent genes of fungi and incorporating them into tobacco in plants, tobacco that continues to emit light from the seedling stage to maturity was born.

It seems that plants incorporating the bacterial bioluminescence gene may have exhibited toxicity, but tobacco that has been genetically engineered using fungal DNA does not have such problems as toxicity. I was not able to see it. `` Overall phenotype,
According to the research team, the tobacco produced by the new experiment is brightest in the young part, producing 1 billion photons per minute. This is about 10 times brighter than a conventional plant that has been genetically modified so that it emits bioluminescence, and it is possible to see the light clearly with the human naked eye.
Also, in the past, a research team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has succeeded in emitting 1 trillion photons per second using a technology called plant nanobionics that penetrates nanoparticles into plant leaves. However, with this method, it is necessary to give chemical substances necessary for light emission from the outside, and the light lasted for only 3.5 hours, which is quite considerable from this research that continued to emit light during most of the growth process. There is a difference.

In the future, it may be possible to reduce the dependence on streetlights by planting plants that emit light outdoors, but to see how plants respond to the external environment, plants that emit light autonomously The research team pointed out that it was useful. For example, if you put a banana peel near the cigarette you made this time, it seems that the cigarette shined brighter in response to ethylene released from the skin, and you can detect the reaction of the plant by observing the light. thing.
Also, luminescence seems to be affected by internal metabolic processes, and the research team argues that bioluminescent plants may provide an interesting method for observing the internal state of plants that can not usually be observed from the outside Did. 'Because luciferin and other substances don't have to be given externally, the autonomous luminescence ability of plants should help experiments with soil-grown plants,' the research team commented. In the future, it seems that they plan to test whether plants that have beautiful flowers such as periwinkle , petunia , and roses can also emit light in the same way.

Related Posts:







