20 rules for learning efficiently

Learning and learning something takes time. Piotr Wozniak, the creator of
Effective learning: Twenty rules of formulating knowledge
https://www.supermemo.com/en/archives1990-2015/articles/20rules
◆ 01: Do not study with difficult-to-understand teaching materials
Many of the learning materials appear to be well-made, and are often difficult to understand. Rather than forcing you to use it someday, you'll need to find the right material for you.
◆ 02: Learn before memorizing
Instead of memorizing explanations and commentary as it is, you need to understand the whole picture of knowledge. For example, when learning about engines, it is important to understand the principle of the engine and learn the role and name of each part instead of memorizing the names of the parts that move the engine from scratch. The whole picture of knowledge does not need to be complete in every detail. Conversely, the bigger picture is better, and the simpler model is easier to understand. You can always acquire detailed knowledge later.
◆ 03: Based on the basics
Basics are more important than anything, and memorizing the basics isn't a waste of time, even if it's obvious. If you forget the basics and proceed with your learning, you will not be able to understand the important things, and re-starting the basics can be a hassle again.
◆ 04: Minimize knowledge
It is effective to split the knowledge you are learning into simple and easy things. For example, if you want to learn about the characteristics of the Dead Sea, say, 'A salt lake at the border between Israel and Jordan, the coastline of which is the lowest point on the earth's surface. It is not efficient to learn in one sentence, such as 'Salt concentration can lift people. Only some organisms such as bacteria can live in the Dead Sea.'
It is effective to learn not by one sentence but by each item as follows.
・ Place of the Dead Sea: Border of Israel and Jordan
・ Lowest point on the ground surface: Dead Sea coastline
・ Dead sea level: about -430m
・ Total length of the Dead Sea: 70km
・ Salt concentration in the Dead Sea: about 30%, 7 times that of the sea
・ Why the Dead Sea can lift people: because of its high salt content.
-Reason for the name Dead Sea: Most creatures cannot live in the Dead Sea.
05: Fill-in-the-blank problem
The fill-in-the-blank problem is effective when it is difficult to divide the knowledge described in 4. You can acquire knowledge quickly by repeating important words and phrases and associating words with explanations. For example, when studying the history of Kaleida, a joint venture between Apple and IBM, 'Kaleida raised $ 40 million from Apple and IBM in 1991. Kaleida's mission was to develop a multimedia programming language. It took three years to develop a scripting language called ScriptX. Kaleida was shut down in 1995. '
It is effective to acquire knowledge by creating a hole-filling question and learning repeatedly as shown below.
Q: Kaleida received $ 40 million in funding from XX (company) in 1991.
A: Apple and IBM
Q: Kaleida's mission is to create XX.
A: Multimedia programming language
Q: In the end, Kaleida has launched a scripting language called xx.
A: ScriptX
Q: It took XX (time) to create ScriptX.
A: 3 years
Q: Kaleida was closed on XX (year).
A: 1995
◆ 07: Use pictures and diagrams
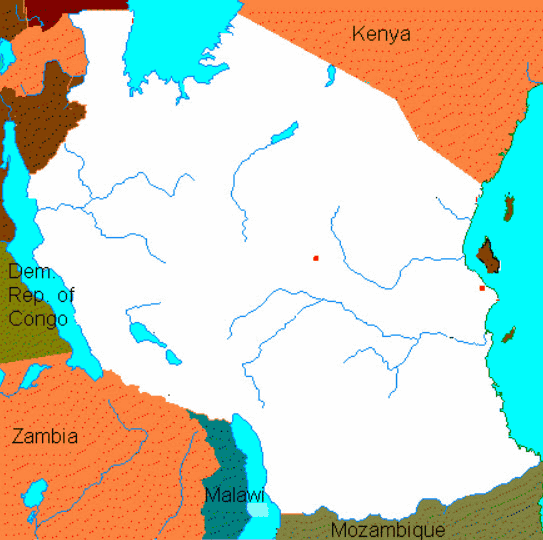
Rather than trying to memorize only sentences, it is effective to use pictures and figures to make them easier to interpret. Human language processing ability is very inferior to visual processing ability, and it can be said that a single picture contains more information than text. For example, rather than asking a question, 'Which country is between Kenya, Zambia, and Mozambique?', It would be easier to see the map below and ask, 'Which country is white?' .
◆ 08: Figure fill-in problem
It is also effective to create a fill-in-the-blank question by combining figures and pictures, just like the fill-in-the-blank question.
◆ 09: Don't remember as a set
It is not efficient to memorize all the member states in order to learn the answer to the question 'What countries are members of the EU?' It is inefficient to memorize a set containing five or more elements as a set. It is effective to divide it into some categories and reduce the number of elements to 5 or less. For example, in the case of EU member states, it is recommended to memorize it by dividing it into the year of membership.
Q: Which countries joined in 1973?
A: Denmark / Ireland
Q: Which countries joined in 1995?
A: Austria, Finland, Sweden
◆ 10: Avoid enumeration
Enumeration is a classic example that is difficult to remember. You should avoid enumeration whenever possible, and remember by filling in the five. For example, instead of enumerating and remembering 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTU VWXYZ' to memorize the alphabetical order, it is effective to learn by filling in the holes as shown below.
Q: A ○○○ E ……
A: BCD

◆ 11: Do not remember similar words at once
Learning something similar can be confusing. For example, it may be difficult to remember the distinction between the word 'historic' and the English word 'historical'. Not only in English, it is also difficult to memorize the optimal dosage of medicines and the list of numbers. As explained in 4 above, it is effective to divide the knowledge to a minimum and remember it.
◆ 12: Memory optimization
When memorizing something, it is more effective to pick up and memorize important words and points rather than memorize each word exactly. You need to determine what information is important and remember only what is important. Duplicate content or useless information only slows down the learning process.
◆ 13: Refer to other knowledge
Learning more than just one piece of knowledge can increase your memory. For example, learning about the Dead Sea mentioned in Section 4 not only about the Dead Sea but also the geography of Israel and Jordan where the Dead Sea is located, so that knowledge will be linked, memories will be strengthened, and more drawers will be increased can do.
◆ 14 : Similar to something
One of the most effective ways to improve memory is to make connections with people around you. For example, there are many effective methods, such as remembering the face of a great man as a familiar person, or speaking with others.
◆ 15: Depends on emotional state
When explaining something, if you can explain it with a shocking example, you can connect knowledge and memory more strongly. In particular, it is said that the connection with emotion is easy to evoke memory, but it is not a very effective means to elicit memory by emotion because it depends on the state of the person.

◆ 16 : Simplification of expression
Although it is recommended to divide the knowledge as described in 4 above, simplifying the explanation of the knowledge will save much input and much reading. By learning less and more accurately, you can increase your learning speed.
◆ 17: Add redundancy
Redundancy is information that is more than necessary or redundant. In Section 4, the knowledge should be minimized, but it is important to acquire a lot of divided knowledge and related information.
◆ 18: Record of information source
With the exception of well-verified and proven knowledge, it is advisable to keep a record of the source when collecting knowledge. Depending on the source, facts and figures may vary. Often, one source publishes information that is completely different from another.
◆ 19 : Date
Research is progressing in a variety of fields, and new discoveries can make mistakes in the knowledge you have learned. It is important to keep track of when you learn with the published materials. In most cases, new discoveries must overwrite outdated knowledge. Keeping the date helps verify your knowledge.
◆ 20: Determine priority
Knowledge is much more than human beings can wear. Therefore, prioritization is essential to acquire high-quality knowledge in the long term. The way you prioritize affects how you want to capture knowledge. This also affects learning speed. If you want to make use of your knowledge, you should learn the basics first. If you just want to pass the exam, you should give priority to the scope and key words of the exam.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by darkhorse_log