New technology to cool the city with zero power consumption by releasing heat towards the sky

by
It was confirmed that `` June 2019 was the hottest June in the history of observation '', and the record of the highest temperature in Paris was updated on July 25, 2019, the heat on a global scale It has been taken. It is effective to use an air conditioner as a countermeasure against heat stroke. However, since the air conditioner consumes enormous amount of power, it is not only negative for the global environment but also a cause of the heat island phenomenon . In the meantime, technology has emerged that releases the heat that falls from the sun into the sky to lower the temperature without electricity consumption.
A polydimethylsiloxane-coated metal structure for all-day radiative cooling | Nature Sustainability
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-019-0348-5
In the future, this electricity-free tech could help cool buildings in metropolitan areas
https://techxplore.com/news/2019-08-future-electricity-free-tech-cool-metropolitan.html
Qiaoqiang Gan, an associate professor at New York State University Buffalo, and others use aluminum plates coated with dimethylpolysiloxane (PDMS) , a type of silicon, to reduce temperature without consuming electricity We have developed a device that can
This is the device developed this time. Under the plastic plate surrounded by a plate to prevent direct sunlight, there is an aluminum plate coated with PDMS, which absorbs heat and releases it to the outside.

The schematic diagram of the device looks something like this.
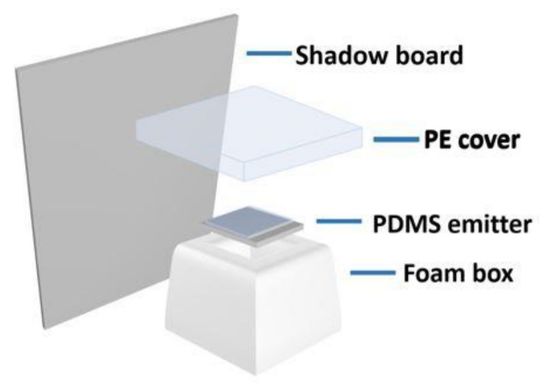
The plate coated with PDMS not only blocks sunlight, but also releases heat by
The mechanism of releasing the internal heat to the outside and lowering the temperature is the same as a refrigerator or air conditioner that cools the inside using a heat pump , but the device developed this time can have directivity in heat radiation If the heat is released toward the sky, the ambient temperature will not be raised by exhaust heat. In addition, it is economical because it does not consume electricity, and it is also characterized by a low environmental impact.
Gan et al.'S research team conducted an outdoor experiment using this device. The following figure is a graph of the three locations where the experiment was conducted and the results. The experiment was performed from the left in a parking lot surrounded by buildings, behind the walls, under the sun. The difference between the ambient temperature and the temperature of the device 20 minutes after the start of the experiment was 2.5 degrees, 7.2 degrees, and 11 degrees from the left, and a high cooling effect was obtained even under hot weather.
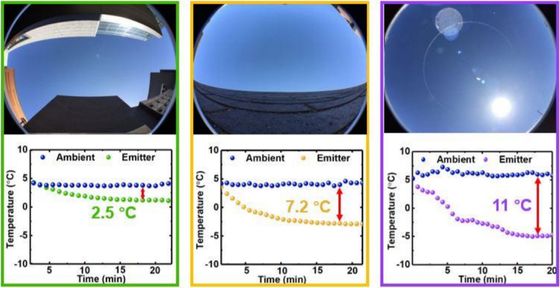
Although this experiment is intended for use in urban areas during the day, it can release heat even without sunlight, so it can provide a cooling effect both day and night. The device is about 25cm square, but PDMS is safe and inexpensive enough to be used as a food additive, so it is easy to enlarge and mass-produce. For this reason, the entire facility can be cooled by deploying many on the roof of the building.
Gan emphasized the advantages of the newly developed passive cooling system, stating, “Practical methods that can be cooled without using electricity can significantly change the world's energy consumption.”
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks