The glass ball found in the clam fossil is evidence that meteorites collided with ancient Earth

A strange thing like a glass ball was found among the bivalve fossils found in the
A first report of microtektites from the shell beds of southwestern Florida-Meyer-2019-Meteoritics & Planetary Science-Wiley Online Library
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/maps.13299
Cosmic pearls: Fossil clams contain evidence of ancient meteorite – Florida Museum Science
https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/science/fossil-clams-contain-evidence-of-ancient-meteorite/
Ethereal 'Pearls' in Fossil Clams Are Evidence of an Ancient Meteorite Hitting Earth
https://www.sciencealert.com/evidence-of-ancient-meteorite-impacts-have-been-found-in-clam-fossils
The Tamiami Formation, located in Florida, USA, has many fossils found in the Plio-Pleistocene strata. Glass beads found in the bivalve fossils found in this layer are generated by heat and seem to be similar to those generated in volcanic activity and industrial activity. However, it is believed that the Tamiami layer did not contain volcanic rocks and there were no volcanoes nearby.
So, how is this glass bead generated? Researchers speculate that it is not caused by the ancient meteorites that collided with the earth. When meteorites collide with the earth, the fragments of the heated meteorites rush into the atmosphere and spatter into the atmosphere, and they fall to the ground and cool down to form tiny glass beads ( tectites ), the researchers say I'm thinking.
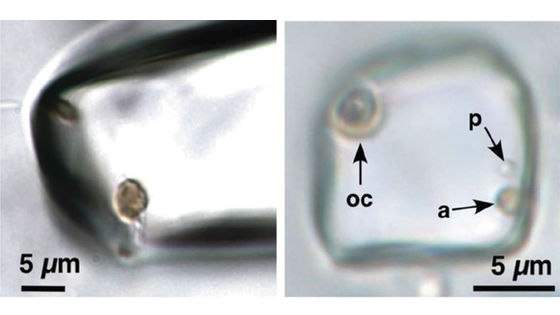
A small amount of tectite found in bivalve molluscs
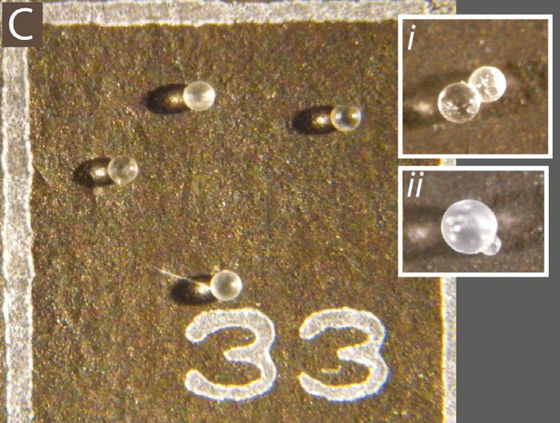

Mike Meyer, a geoscientist at Harrisburg University, was collecting
Meyer seems to have collected as many as 83 glass beads from the clam fossil, but it seems that the glass beads have only been stored for more than 10 years because there are other research materials. However, with time to finally examine the glass ball, Meyer starts a more detailed investigation.
Meyer had to deposit a glass ball on a small patch in order to examine the tektites found in the fossil clam using light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Tektite is so small that it is difficult to pinch. In such a case, it seems that a lot of techniques are taken to lick the object with the tongue and replace it with 'glue', and Meyer seems to have piled it up on the patch by gently licking Tektite. 'I've accidentally eaten some texite,' Meyer says of the process.

Photograph the tektites found in the fossil of clam using light microscope and SEM, and analyze the physical properties. In order to analyze the composition, the research team seems to use SEM,
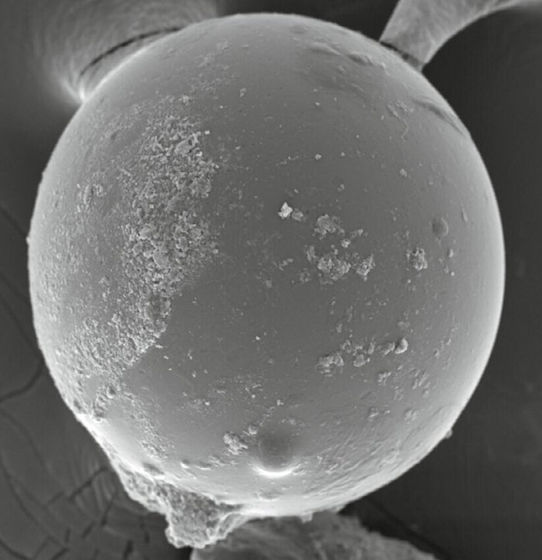
Analyzes the physical properties of tektite compared to volcanic rocks and glass beads produced by industrial processes. While it is not impossible for Florida to have glass beads produced by industrial processes, it is extremely unlikely that they will be incorporated into the clam fossil. Clams die for a while after leaving their shells open, but sediments build up on them and eventually they are tightly closed. It is clear that clams are buried by sediments much earlier than humans start industrial activities, so it is clear that the glass beads found in fossils are not made with modern technology.
In addition, the size, shape, and chemical composition also differ from the glass beads produced by the industrial process. Furthermore, it seems that the composition of the particles was also impossible to generate from the volcano. Therefore, it is thought that the glass ball found in the clam is either a minute meteorite flying from space or a tektite produced by the collision of the meteorites.
Then, it was found from the chemical composition that it contained a large amount of sodium, from which the possibility of being micrometeorites was also excluded, and it was revealed that the glass beads were tectite. The reason why micrometeorites do not contain a large amount of sodium is that the surface is overheated and most minerals are evaporated when they enter the atmosphere.
In addition, since tektite found in clams contains a large amount of sodium, it is speculated that meteorites that collided with the earth in ancient times fell to near salt deposits and the sea.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii