Why does the laser beam draw a straight line?

ByJim Stanton
Unlike natural light, a laser draws a linear orbit, concentrates energy on one point and can apply force, so it is widely used for research applications, industrial applications, medical applications and so on. However, understanding the laser in detail is a bit hurdley. However, we have published many physical-related movies on YouTubeminutephysicsIf the channel has a published movie, you can understand the mechanism of the laser in an easy-to-understand way.
How lasers work (in theory) - YouTube
Preparation for making a laser gathers a lot of atoms and gives energy.
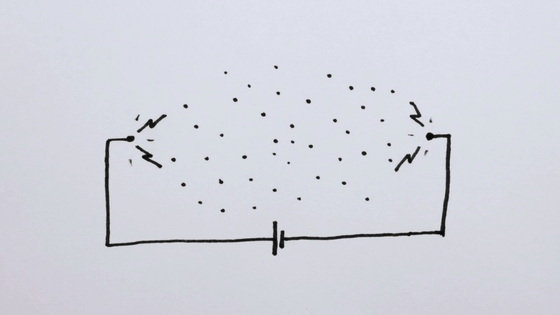
When one of the atoms emits photons that are the source of light, this photon passes over the other atoms and emits photons so that each atom also becomes chained.

Here, do not leave the photons once released.
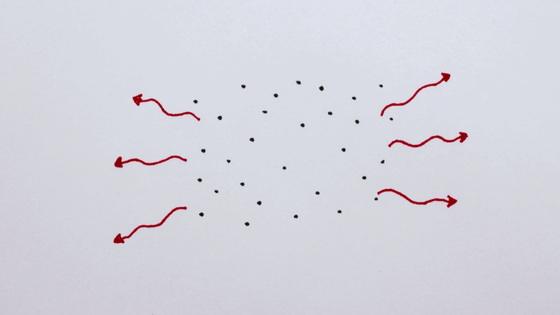
Keep it confined with two mirrors and keep bouncing back and forth, a lot of atoms are stimulated and a stronger light is born. In other words, if we can continue giving energy to atoms in this state, we can emit light forever.
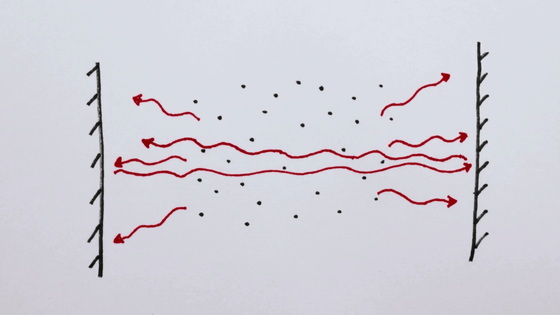
So just pass the photons, why do atoms emit photons?

The answer is simple. Let's first think about turning over two coins. The probability that the two coins are in the same state and the probability that they are in different states are 50% each.

However, photons can not distinguish one by one like a coin. Just like a coin, considering turning a photon upside down, there are two ways for photons to be in the same state, but only one way is in a different state. Therefore, photons tend to be in the same state.

In other words, when the emitted photons pass through the atoms where energy is stored, photons in the same state from the atoms are easy to jump out.

And because the two photons want to spend them together, they proceed in the same direction in exactly the same way.

In other words, it continues to bounce a lot of photons between the mirrors in exactly the same state, and finally when opening a small hole and releasing it, it will be able to emit a laser beam in a straight line trajectory.

Related Posts: