Ticks that kill even cows with massive blood feeding are proliferating in clones

by
Phytophagid ticks are parasitic mites that attach to cows, dogs, humans, etc. from the bushes and suck blood, are widely distributed in Southeast Asia and Australia, and inhabit throughout Japan even in Japan. The presence of such a tick was also confirmed in the United States, and it was found to be proliferating in parthenogenesis without mating.
State Veterinarian reminds livestock and pet owners to watch out for ticks
https://www.ncagr.gov/paffairs/release/2019/StateVeterinarianremindslivestockandpetownerstowatchoutforticks.htm
Clinical Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic Haemaphysalis longicornis Is in the United States and Biting Humans: Where Do We Go From Here?
https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/cid/ciz451/5509426?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Savage tick-clone armies are sucking cows to death; experts fear for humans | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/science/2019/07/savage-tick-clone-armies-are-sucking-cows-to-death-experts-fear-for-humans/
On July 8, 2019, it was discovered that five cattle were dead in North Carolina in the United States. At the time of discovery, more than 1000 ticks were attached to the body of the cow, and the veterinarian confirmed the cause of death as 'acute anemia due to tick feeding'.
Once isolated on the host's body surface and started blood-sucking after being attached to the host's body surface, the flat-tailed tick, which is called 'Asian longhorned tick', sucks up an amount of blood that is about 3 mm in length and more than three times the length. I will. It has been reported that the blood feeding period is long and the blood feeding has been continued for 19 days which is much longer than the average tick period of 7 days. As a result, the host animal is subjected to tremendous stress and growth inhibition, eventually leading to blood loss and death.
Female winged tick tick in a non-feeding state
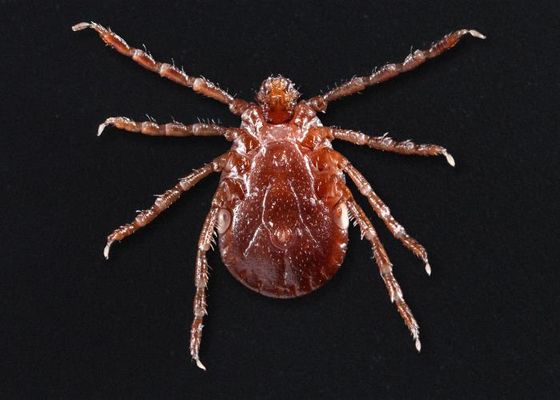

by James Gathany
What is even more troublesome is that this mite is capable of breeding by parthenogenesis without mating. Due to this nature, one female can produce over 2000 new animals in a few weeks.
In addition, Phytophagid ticks are also known to mediate infections such as severe fever thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTS virus) and Japanese spotted fever .
Dr. Michael Neault of the North Carolina State Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services said, “Because the long-sleeved clothing has been in place, after returning from the office, it is said that the plague is already confirmed in more than 10 states in the United States. Please take a shower without putting it and try for prevention of epidemics. '
Related Posts:
in Creature, Posted by log1l_ks