A study to accurately predict aftershocks occurring after the earthquake using AI

The Osaka prefecture northern earthquake that occurred on June 18, 2018 showed a shake of less than 6 shaking intensity, but the aftershocks with a seismic intensity of 1 or more observed after the main shock were 56 times, the largest aftershocks had the maximum seismic intensity 4 It was. Google is conducting a research to predict aftershocks that occur many times after such a large earthquake occurs, using AI.
Deep learning of aftershock patterns following large earthquakes | Nature
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0438-y
Forecasting earthquake aftershock locations with AI-assisted science
https://www.blog.google/technology/ai/forecasting-earthquake-aftershock-locations-ai-assisted-science/
Earthquakes first occurred with a " main shock ", followed by " aftershocks " for several times. Normally, aftershocks are less severe than the main shock, but depending on the timing, activities for reconstruction may be severely hindered. However, it is difficult to accurately predict the timing and magnitude of aftershocks.
So, Phoebe DeVries, a graduate of Harvard University, is teaming up with machine learning experts working at Google and is trying to predict the location of aftershocks using deep learning. Although it seems that research is still in progress, DeVries has published the results of the research in the science journal Nature .
DeVries et al. Research team started from gathering data on 118 major earthquakes that have occurred all over the world. Data is collected as a data set for AI learning. Collected data is visualized, for example, in the case of the Randers earthquake (magnitude 7.3) occurred in the state of California, USA in 1992, it is expressed as follows. A plane where colors such as blue, red and yellow are lined up is a main shock, a translucent red cube floating in the main shock shows a aftershock.

In the research, neural networks are used to analyze the positional relationship between static stress changes caused by the main shock and aftershocks. And it seems that the algorithm succeeded in identifying useful patterns in analysis. Based on this "useful pattern", a model was created to accurately predict the location of aftershocks in the research. According to the research team "Although this system is still inaccurate", it is a major step in the aftershock forecasting, "The prediction system based on machine learning is to notify evacuation areas to areas that are exposed to the risk of aftershocks It will be useful ".
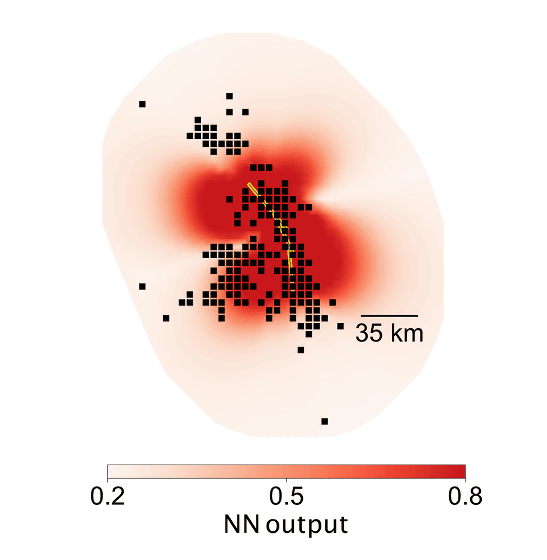
In the following image, the aftershock prediction system developed by the research team output data predicted about the aftershocks that occur after "mainshock data of the Randers earthquake". The dark red part is the region that the system predicted "aftershocks will occur", and the black dot shows the place where aftershocks actually occurred. The yellow line at the center of the image shows the fault that occurred when the main shock occurred.
In the research, unintended results are also present, and it is clear that the developed system helps to identify important " physical quantities " at the time of earthquake occurrence. When a neural network is applied to the data set, it is said that prediction results are not output, but a combination of specific factors that are important for prediction will be identified. "This is because, in order to better understand natural phenomena It opens up new possibilities for finding potential physics theory, "the research team wrote.
Related Posts: