"Overlining" by pushing is important for fixing the learned knowledge to the brain

ByCollegeDegrees 360
It is well known that it is important to learn repeatedly in order to learn something, but knowledge is fixed to the brain by learning by further pushing even after getting acquainted It has been clarified that there is an effect to make it.
Overlearning hyperstabilizes a skill by rapidly making neurochemical processing inhibitory-dominant: Nature Neuroscience: Nature Research
http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nn.4490.html
How to activate your brain's ability to learn | Popular Science
http://www.popsci.com/study-brain-overlearning-to-master-skills
From 'overlearning' to going barefoot: how to learn better | Science | The Guardian
https://www.theguardian.com/science/shortcuts/2017/jan/31/overlearning-to-going-barefoot-how-to-learn-better
According to the paper published in the scientific journal "Nature Neuroscience", the brain learns the same content again after learning a certain amount, so that the function of "fixing" the content acquired at the brain cell level about. Research teams by Professor Watanabe Takeo of Professor Cognitive Linguistic Psychology Department of Brown University in the United States have conducted research on the brain learning by visual training and repeated the same contents after learning to fix to the brain It is made clear that the conversion will be carried out.
In the study, we gave multiple subjects with a linear pattern called "Gabor patch" in two subject groups and let them learn. At the time of learning, training in one group is terminated when it is confirmed that the content has been acquired. In that case, on average, training is finished with the eighth learning. After a 30-minute break, let me learn another content in the same way and finish the first day. On the next day, when the subjects were tested on the contents learned, although they showed good results with respect to the content of the learning that took place after the break, they learned nothing about the content that was first learned He was able to show only the same level of achievement as not being able to do.

About this result Professor Watanabe stated that "In a situation where training has been completed immediately after mastering a new skill, the field related to that skill is usually in the brain that is still in a plastic state." This means that the mode to acquire new skills in the brain is continuing, and that the memory is not yet established. And if you train another new skill in this state, you know that the old memory will be overwritten by the new memory. This is due to the memory interference that old memories are prevented by new memories,Counter inhibitionIt is showing that it is happening.
In the other group of subjects, "over-learning" is conducted in which the same content is repeatedly learned eight more times from the state where it is confirmed that the first learning has been performed and a total of 16 subjects are learned I did. After a half-hour break, we also carried out a cycle of learning different contents as well.
And the next day, we conducted a test on what we learned in the same way. Then, the test on the first content clearly gave better results than the group described above. This means that by implementing "over-learning" about 20 minutes after learning, memory is successfully established in the brain. Also, it is confirmed that "memory interference" has not occurred in the test on the second content as described above. However, I found that the results of the test were somewhat lower when compared to the groups that did not overlaunt.
To summarize the results, the group that does not overlaunt leave good results in the second test instead of having the results in the first test. The group which overworked one, leaving good results in the first test, and being slightly inferior to the other in the second test, was able to show poor results. Taking these results together, we can conclude that the group that over-learned has comprehensively good results.
To investigate this difference, Professor Watanabe is a type of MRI that can examine ingredients of substances in the brainMR spectroscopyWe are investigating the behavior of the brain using. In order to know the work in the brain, we investigate areas that are activated by visualizing blood flow in the brainFMRIIn many cases, the research team tracks which substances such as carbon and nitrogen exist in the brain by using MR spectroscopy, and where the neurotransmitter is working It is said that it analyzed whether it is.
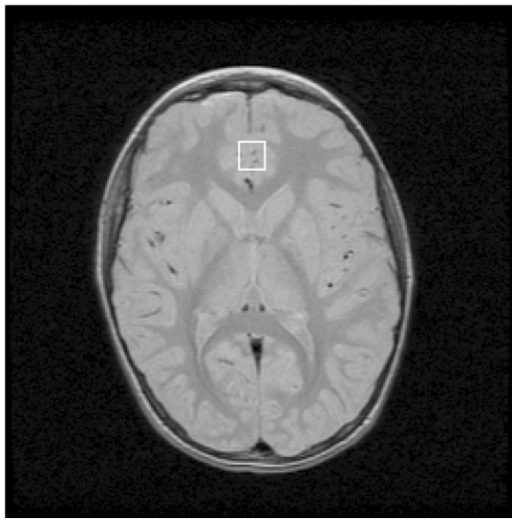
In the verification using MRS, observe the difference in the brain by letting the above-mentioned learning to two groups. However, at this time, we only let you learn about one subject, only one learning in one group, and sixteen learning "over-learning" in the other group. The research team scanned the brains of subjects by MRS before learning, 30 minutes after learning, and 3.5 hours later, and made the test on the second day as well as the first experiment.
As a result of this study, it was confirmed that the excitability by glutamate is mainly high in the brain of the group not undergoing over-learning. Glutamate has the effect of "making it easier to learn" by increasing the plasticity of the brain. On the other hand, it is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain of the over-learned groupGABAIt is confirmed that many exist.
Professor Watanabe stated about this difference, "By performing over-learning, the state of the brain rapidly changes from plastic to stable." In other words, this indicates that by over-learning, the brain has a function of fixing memory and making it difficult to overwrite it. In order to ensure that one acquires one thing, it can be said that making repeated learning from the stage of learning completion to some extent is effective.
However, Professor Robert Goldstone of Indiana University points out that this over-learning should not be trusted excessively. Another research result showing that the effect of over-learning disappears in about 4 weeks is shown, and for over-learningInterval repetitionIt is possible to complete an effective learning for the first time by combining learning with the other.
Papers by the research team can be viewed from the following links.
Overlearning hyperstabilizes a skill by rapidly making neurochemical processing inhibitory-dominant: Nature Neuroscience: Nature Research
Related Posts:







